rna-tools¶
RNA Sequence¶
RNA Sequence with secondary structure prediction methods.
This tool takes a given sequence and returns the secondary structure prediction provided by 5 different tools: RNAfold, RNAsubopt, ipknot, contextfold and centroid_fold. You must have these tools installed. You don’t have to install all tools if you want to use only one of the methods.
It’s easy to add more methods of your choince to this class.
Installation¶
Depends on what tools you want to use, follow the instructions below.
ContextFold¶
https://www.cs.bgu.ac.il/~negevcb/contextfold/
needs Java. Try this on Ubuntu 14-04 https://askubuntu.com/questions/521145/how-to-install-oracle-java-on-ubuntu-14-04 Single chain only!
ViennaRNA¶
https://www.tbi.univie.ac.at/RNA/
For OSX install from the binary Installer from the page.
ipknot OSX¶
https://github.com/satoken/homebrew-rnatools
If one encounters a problem:
[mm] Desktop$ /usr/local/opt/bin/ipknot
dyld: Library not loaded: /usr/local/opt/glpk/lib/libglpk.40.dylib
Referenced from: /usr/local/opt/bin/ipknot
Reason: image not found
[1] 51654 abort /usr/local/opt/bin/ipknot
the solution is:
brew install glpk # on OSX
RNA Structure¶
http://rna.urmc.rochester.edu/
Works with 5.8.1; Jun 16, 2016.
Download http://rna.urmc.rochester.edu/RNAstructureDownload.html and untar it in <RNA_PDB_TOOLS>/opt/RNAstructure/; run make, the tools will be compiled in a folder exe. Set up DATPATH in your bashrc to <RNA_PDB_TOOLS>/opt/RNAstructure/data_tables DATAPATH=/home/magnus/work/src/rna-pdb-tools/opt/RNAstructure/data_tables/ (read more http://rna.urmc.rochester.edu/Text/Thermodynamics.html). RNAstructure can be run with SHAPE restraints, read more http://rna.urmc.rochester.edu/Text/File_Formats.html#Constraint about the format. The file format for SHAPE reactivity comprises two columns. The first column is the nucleotide number, and the second is the reactivity. Nucleotides for which there is no SHAPE data can either be left out of the file, or the reactivity can be entered as less than -500. Columns are separated by any white space.
MC-Sym¶
FAQ¶
Does it work for more than one chain??? Hmm.. I think it’s not. You have to check on your own. –magnus
TIPS¶
Should you need to run it on a list of sequences, use the following script:
from rna_tools import Seq
f = open("listOfSequences.fasta")
for line in f:
if line.startswith('>'):
print line,
else:
print line,
s = Seq.Seq(line.strip()) # module first Seq and class second Seq #without strip this has two lines
print s.predict_ss(method="contextfold"),
#print s.predict_ss(method="centroid_fold")
Todo
This calss should be renamed to RNASeq and merged with RNASeq class from RNAalignment
- class rna_tools.Seq.RNASequence(seq, ss='', name='rna_seq')[source]¶
RNASequence.
Usage:
>>> seq = RNASequence("CCCCUUUUGGGG") >>> seq.name = 'RNA03' >>> print(seq.predict_ss("RNAfold", constraints="((((....))))")) >RNA03 CCCCUUUUGGGG ((((....)))) ( -6.40)
- eval(ss='', no_dangling_end_energies=False, verbose=False)[source]¶
Evaluate energy of RNA sequence.
- Parameters:
ss (optional) –
no_dangling_end_energies (Boolean) –
verbose (Boolean) –
- Returns:
Energy (float)
The RNAeval web server calculates the energy of a RNA sequence on a given secondary structure. You can use it to get a detailed thermodynamic description (loop free-energy decomposition) of your RNA structures.
Simply paste or upload your sequence below and click Proceed. To get more information on the meaning of the options click the help symbols. You can test the server using this sample sequence/structure pair.
An equivalent RNAeval command line call would have been:
RNAeval -v -d0 < input.txt
Read more: <http://rna.tbi.univie.ac.at//cgi-bin/RNAWebSuite/RNAeval.cgi>
- get_foldability(ss='', verbose=False)[source]¶
Calculate foldability based on EntRNA.
Steps:
parse SS into basepairs,
calculate foldabilty
Configuration:
Set ENTRNA_PATH to the folder where ENTRNA_predict.py is.
Cmd wrapper in here:
python ENTRNA_predict.py --seq_file pseudoknotted_seq.txt --str_file pseudoknotted_str.txt
Su, C., Weir, J. D., Zhang, F., Yan, H., & Wu, T. (2019). ENTRNA: a framework to predict RNA foldability. BMC Bioinformatics, 20(1), 1–11. http://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-019-2948-5
- predict_ss(method='RNAfold', constraints='', enforce_constraint=False, shapefn='', explore='', verbose=0, path='')[source]¶
Predict secondary structure of the seq.
- Parameters:
method – {mcfold, RNAfold}
onstraints –
shapefn (str) – path to a file with shape reactivites
verbose (boolean) –
It creates a seq fasta file and runs various methods for secondary structure prediction. You can provide also a constraints file for RNAfold and RNAsubopt.
Methods that can be used with contraints: RNAsubopt, RNAfold, mcfold.
Methods that can be used with SHAPE contraints: RNAfold.
ContextFold
Example:
$ java -cp bin contextFold.app.Predict in:CCCCUUUGGGGG CCCCUUUGGGGG ((((....))))
It seems that a seq has to be longer than 9. Otherwise:
$ java -cp bin contextFold.app.Predict in:UUUUUUGGG Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 10 # this is OK $ java -cp bin contextFold.app.Predict in:CCCCUUUGGG CCCCUUUGGG .(((...)))
RNAstructure
Example:
>>> seq = RNASequence("GGGGUUUUCCC") >>> print(seq.predict_ss("rnastructure")) > ENERGY = -4.4 rna_seq GGGGUUUUCCC ((((...))))
and with the shape data:
>>> print(seq.predict_ss("rnastructure", shapefn="data/shape.txt")) > ENERGY = -0.2 rna_seq GGGGUUUUCCC .(((....)))
the shape data:
1 10 2 1 3 1
You can easily see that the first G is unpaired right now! The reactivity of this G was set to 10. Worked!
MC-Fold
MC-Fold uses the online version of the tool, this is very powerful with constraints:
rna_seq acucggcuaggcgaguauaaauagccgucaggccuagcgcguccaagccuagccccuucuggggcugggcgaagggucggg ((((........)))).......((((..............(((((((((((((((....)))))))))))))))..)))) curl -Y 0 -y 300 -F "pass=lucy" -F mask="((((........)))).......((((..............(((((((((((((((....)))))))))))))))..))))" -F sequence="acucggcuaggcgaguauaaauagccgucaggccuagcgcguccaagccuagccccuucuggggcugggcgaagggucggg" https://www.major.iric.ca/cgi-bin/MC-Fold/mcfold.static.cgi mcfold::energy best dynamics programming: -53.91 (-53.91, '((((........)))).......((((..............(((((((((((((((....)))))))))))))))..))))') curl -Y 0 -y 300 -F "pass=lucy" -F mask="((((........)))).......((((..............((((((((((..............))))))))))..))))" -F sequence="acucggcuaggcgaguauaaauagccgucaggccuagcgcguccaagccuagccccuucuggggcugggcgaagggucggg" https://www.major.iric.ca/cgi-bin/MC-Fold/mcfold.static.cgi mcfold::energy best dynamics programming: -34.77 (-34.77, '((((........)))).......((((..............((((((((((..............))))))))))..))))') acucggcuaggcgaguauaaauagccgucaggccuagcgcguccaagccuagccccuucuggggcugggcgaagggucggg ((((........)))).......((((..............(((((((((((((((....)))))))))))))))..)))) curl -Y 0 -y 300 -F "pass=lucy" -F mask="((((xxxxxxxx))))xxxxxxx((((xxxxxxxxxxxxxx((((((((((xxxxxxxxxxxxxx))))))))))xx))))" -F sequence="acucggcuaggcgaguauaaauagccgucaggccuagcgcguccaagccuagccccuucuggggcugggcgaagggucggg" https://www.major.iric.ca/cgi-bin/MC-Fold/mcfold.static.cgi mcfold::energy best dynamics programming: -34.77 (-34.77, '((((........)))).......((((..............((((((((((..............))))))))))..))))') acucggcuaggcgaguauaaauagccgucaggccuagcgcguccaagccuagccccuucuggggcugggcgaagggucggg ((((........)))).......((((..............(((((((((((((((....)))))))))))))))..)))) curl -Y 0 -y 300 -F "pass=lucy" -F mask="((((********))))*******((((**************((((((((((**************))))))))))**))))" -F sequence="acucggcuaggcgaguauaaauagccgucaggccuagcgcguccaagccuagccccuucuggggcugggcgaagggucggg" https://www.major.iric.ca/cgi-bin/MC-Fold/mcfold.static.cgi mcfold::energy best dynamics programming: -77.30 (-71.12, '(((((((..))))))).......((((((.(((...)))..(((((((((((((((....)))))))))))))))))))))') acucggcuaggcgaguauaaauagccgucaggccuagcgcguccaagccuagccccuucuggggcugggcgaagggucggg ((((........)))).......((((..............(((((((((((((((....)))))))))))))))..)))) curl -Y 0 -y 300 -F "pass=lucy" -F mask="((((**[[[[[**))))*******((((****]]]]]****(((((((((((((((****)))))))))))))))**))))" -F sequence="acucggcuaggcgaguauaaauagccgucaggccuagcgcguccaagccuagccccuucuggggcugggcgaagggucggg" https://www.major.iric.ca/cgi-bin/MC-Fold/mcfold.static.cgi mcfold::energy best dynamics programming: -77.30 ('-77.30', '((((**[[[[[**))))*******((((****]]]]]****(((((((((((((((****)))))))))))))))**))))')
explore
The sub-optimal search space can be constrained within a percentage of the minimum free energy structure, as MC-fold makes use of the Waterman-Byers algorithm [18, 19]. Because the exploration has an exponential time complexity, increasing this value can have a dramatic effect on MC-Fold’s run time.
Parisien, M., & Major, F. (2009). RNA Modeling Using the MC-Fold and MC-Sym Pipeline [Manual] (pp. 1–84).
RNA Secondary Structure¶
Secondary structure analysis
- rna_tools.SecondaryStructure.draw_ss(title, seq, ss, img_out, resolution=4, verbose=False)[source]¶
Draw Secondary Structure using VARNA (you need correct configuration for this).
If everything is OK, return None, if an error (=exception) return stderr.
Usage:
>>> seq = 'GGAAACC' >>> ss = '((...))' >>> img_out = 'output/demo.png' >>> draw_ss('rna', seq, ss, img_out) >>> print('Made %s' % img_out) Made output/demo.png
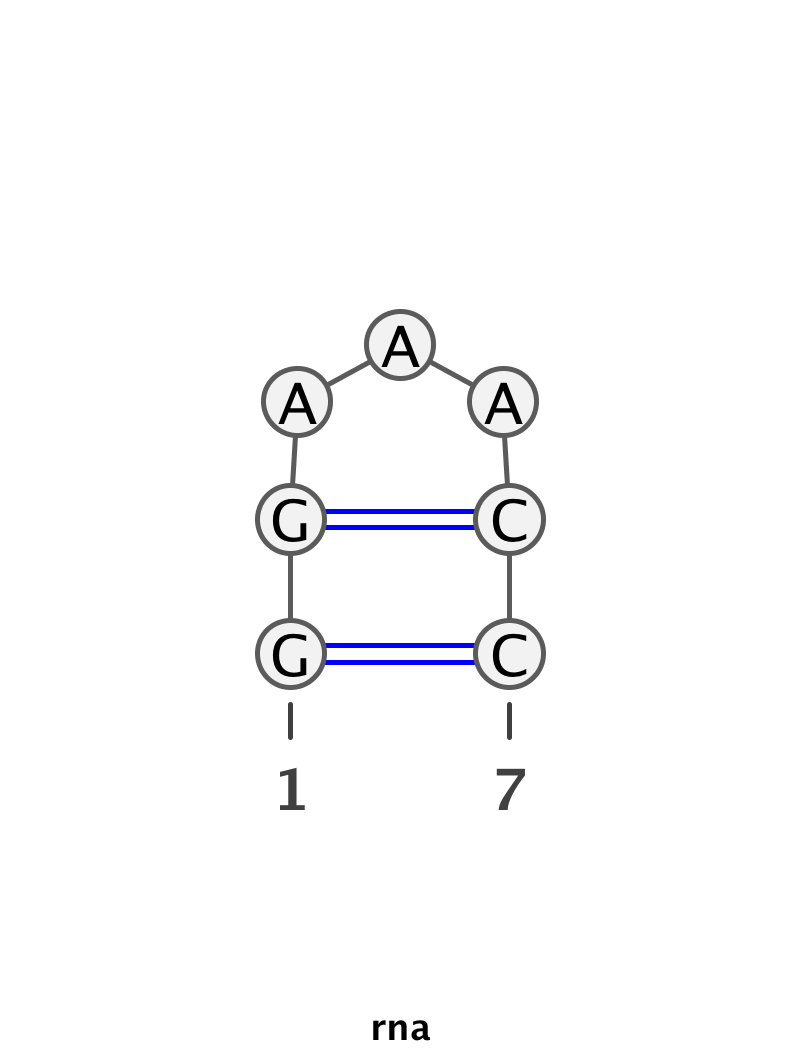
Can be used with http://geekbook.readthedocs.io/en/latest/rna.html
- rna_tools.SecondaryStructure.parse_vienna_to_pairs(ss, remove_gaps_in_ss=False)[source]¶
Parse Vienna (dot-bracket notation) to get pairs.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
(pairs, pairs_pk)
- Return type:
list of two lists
Examples:
>>> parse_vienna_to_pairs('((..))') ([[1, 6], [2, 5]], []) >>> parse_vienna_to_pairs('(([[))]]') ([[1, 6], [2, 5]], [[3, 8], [4, 7]]) >>> parse_vienna_to_pairs('((--))') ([[1, 6], [2, 5]], []) >>> parse_vienna_to_pairs('((--))', remove_gaps_in_ss=True) ([[1, 4], [2, 3]], []) >>> parse_vienna_to_pairs('((((......') Traceback (most recent call last): File "/usr/lib/python2.7/doctest.py", line 1315, in __run compileflags, 1) in test.globs File "<doctest __main__.parse_vienna_to_pairs[4]>", line 1, in <module> parse_vienna_to_pairs('((((......') File "./SecondaryStructure.py", line 106, in parse_vienna_to_pairs raise ExceptionOpenPairsProblem('Too many open pairs (()) in structure') ExceptionOpenPairsProblem: Too many open pairs (()) in structure
rna_dot2ct.py¶
The output file is <input-file>.ct
Wrapper to
RNAstructure: software for RNA secondary structure prediction and analysis. (2010). RNAstructure: software for RNA secondary structure prediction and analysis., 11, 129. http://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-11-129
usage: rna_dot2ct.py [-h] [-v] file
- file¶
Input is: >seq aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa ((…((((((((((…….)))))))))).))
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- -v, --verbose¶
be verbose
Secondary structure format conversion¶
rna_convert_pseudoknot_formats
Run this as:
python rna-pk-simrna-to-one-line.py test_data/simrna.ss
Convert:
> a
....((.(..(((....)))..((((.(.........).)))....).)).......((((......))))
..............................((((...................))))..............
to:
> a
....((.(..(((....)))..((((.(..[[[[...).)))....).))...]]]]((((......))))
and:
>2 chains
(((((......)))))........(.((....(.......)..(((. .)))...)).)
.....((((((......................))))))........ ...........
to:
>2 chains
((((([[[[[[)))))........(.((....(]]]]]].)..(((. .)))...)).)
and:
> b
..(.......(((....)))..((((.(.........).))))).............((((......))))
....((.(......................................).)).....................
..............................((((...................))))..............
to:
> b
..(.[[.[..(((....)))..((((.(..{{{{...).)))))..].]]...}}}}((((......))))
and it works with VARNA:
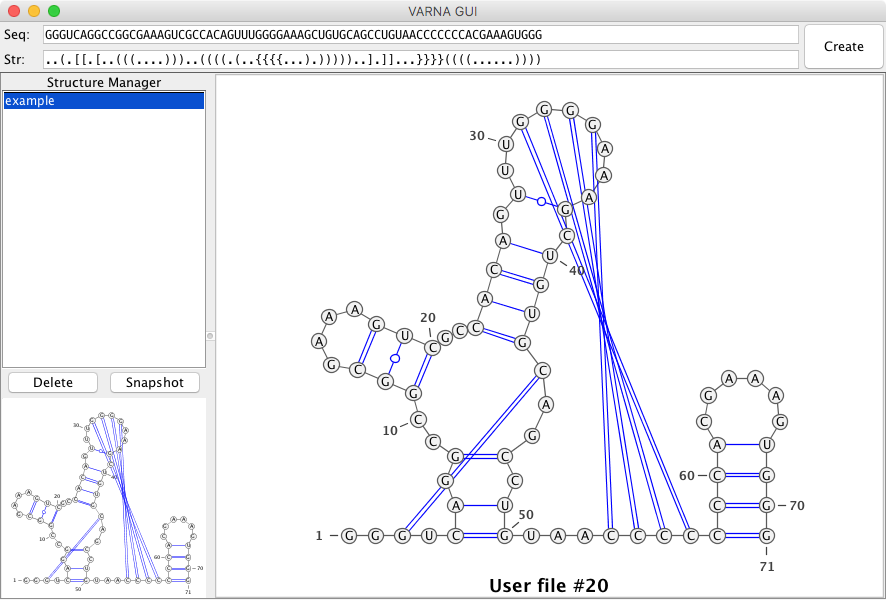
Convert a secondary structure with a pk to the SimRNA format:
rna_convert_pseudoknot_formats git:(master) ✗ python rna_ss_pk_to_simrna.py test_data/ss_with_pk.ss
((((([[[[[[)))))........(.((....(]]]]]].)..(((. .)))...)).)
(((((......)))))........(.((....(.......)..(((. .)))...)).)
.....((((((......................))))))........ ...........
Search¶
Blast PDB¶
A super-simple wrapper around Blast on the PDB db (online).
- class rna_tools.BlastPDB.BlastPDB(seq)[source]¶
BlastPDB - run Blast online on the PDB database.
This can be used in Jupiter based RNA notebooks, e.g. https://github.com/mmagnus/rna-pdb-tools/blob/master/rp18.ipynb
Warning: getBlastPDB1 has been permanently removed as part of our announced shutdown on December 9th, 2020. https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/rest/getBlastPDB1
Usage:
>>> p = BlastPDB('GGGUCAGGCCGGCGAAAGUCGCCACAGUUUGGGGAAAGCUGUGCAGCCUGUAACCCCCCCACGAAAGUGGG') >>> p.search() >>> p.result u'<HTML>\n<TITLE>BLAST Search Results</TITLE>...
- Parameters:
seq – string
Rfam Search¶
A super-simple wrapper around cmscan (Infernal) on local Rfam database.
- class rna_tools.RfamSearch.RfamSearch[source]¶
RfamSearch (local).
Rfam is a collection of multiple sequence alignments and covariance models representing non-coding RNA families. Rfam is available on the web http://rfam.xfam.org/. The website allow the user to search a query sequence against a library of covariance models, and view multiple sequence alignments and family annotation. The database can also be downloaded in flatfile form and searched locally using the INFERNAL package (http://infernal.wustl.edu/). The first release of Rfam (1.0) contains 25 families, which annotate over 50 000 non-coding RNA genes in the taxonomic divisions of the EMBL nucleotide database.
Infernal (“INFERence of RNA ALignment”) is for searching DNA sequence databases for RNA structure and sequence similarities. It is an implementation of a special case of profile stochastic context-free grammars called covariance models (CMs). A CM is like a sequence profile, but it scores a combination of sequence consensus and RNA secondary structure consensus, so in many cases, it is more capable of identifying RNA homologs that conserve their secondary structure more than their primary sequence.
Infernal cmscan is used to search the CM-format Rfam database.
Setup:
download the database from ftp://ftp.ebi.ac.uk/pub/databases/Rfam/CURRENT (file: Rfam.cm.gz, ~30mb)
install http://eddylab.org/infernal/
set up
RFAM_DB_PATHin the config file of rna-tools.compress Rfam.cm
Example of compressing the database:
$ cmpress Rfam.cm Working... done. Pressed and indexed 3016 CMs and p7 HMM filters (3016 names and 3016 accessions). Covariance models and p7 filters pressed into binary file: Rfam.cm.i1m SSI index for binary covariance model file: Rfam.cm.i1i Optimized p7 filter profiles (MSV part) pressed into: Rfam.cm.i1f Optimized p7 filter profiles (remainder) pressed into: Rfam.cm.i1p
Cite: Nawrocki and S. R. Eddy, Infernal 1.1: 100-fold faster RNA homology searches, Bioinformatics 29:2933-2935 (2013).
RNA Alignment¶
RNAalignment - a module to work with RNA sequence alignments.
To see a full demo what you can do with this util, please take a look at the jupiter notebook (https://github.com/mmagnus/rna-pdb-tools/blob/master/rna_tools/tools/rna_alignment/rna_alignment.ipynb)
Load an alignment in the Stockholm:
alignment = ra.RNAalignment('test_data/RF00167.stockholm.sto')
or fasta format::
import rna_alignment as ra
alignment = ra.fasta2stokholm(alignment.fasta)
alignment = ra.RNAalignment
Parameters of the aligmnent:
print(alignment.describe())
Consensus SS:
print(alignment.ss_cons_with_pk)
Get sequnce/s from teh aligment:
>>> seq = a.io[0]
RNASeq¶
- class rna_tools.tools.rna_alignment.rna_alignment.RNASeq(id, seq, ss=None)[source]¶
RNASeq.
- Parameters:
Warning
>>> if 'EF' in s.id: print('Y') Y >>> if 'EF' in s: print('Y') # nothing
- draw_ss(title='', verbose=False, resolution=1.5)[source]¶
Draw secondary structure of RNA with VARNA.
VARNA: Visualization Applet for RNA A Java lightweight component and applet for drawing the RNA secondary structure
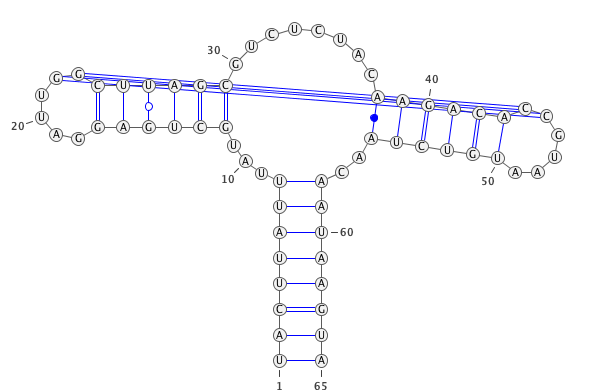
Cite: VARNA: Interactive drawing and editing of the RNA secondary structure Kevin Darty, Alain Denise and Yann Ponty Bioinformatics, pp. 1974-197,, Vol. 25, no. 15, 2009
- get_conserved(consensus, start=0, to_pymol=True, offset=0)[source]¶
Start UCGGGGUGCCCUUCUGCGUG————————————————–AAGGC-UGAGAAAUACCCGU————————————————-AUCACCUG-AUCUGGAU-AAUGC XXXXXXXXXXXXGXGXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX—————————-XXXXX-XCUGAGAXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX———————————-XXXXXXXX-XXXXXXXX-ACXUG
- remove_gaps(check_bps=True, only_canonical=True, allow_gu=True)[source]¶
Remove gaps from seq and secondary structure of the seq.
- Parameters:
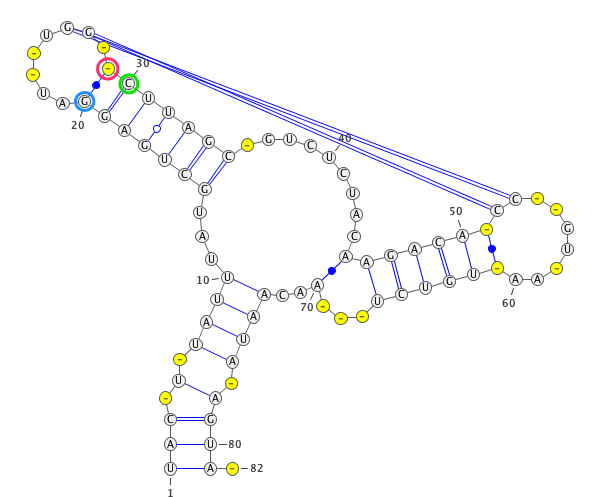
A residue “paired” with a gap.
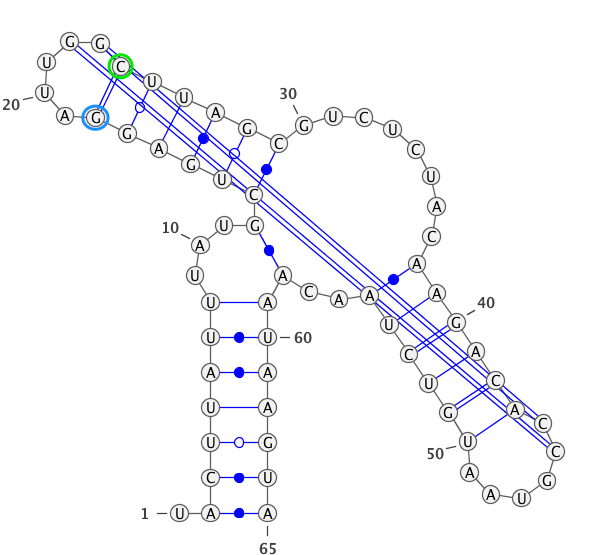
paired with any residues (in the blue circle). If yes, then this residues is unpair (in this case
)->.).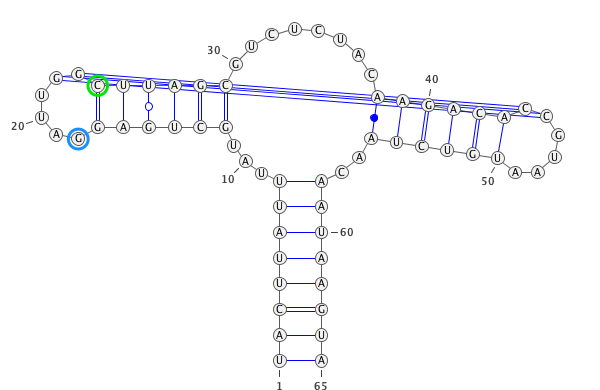
if
only_canonical(by default) is True then only GC, AU can be paired.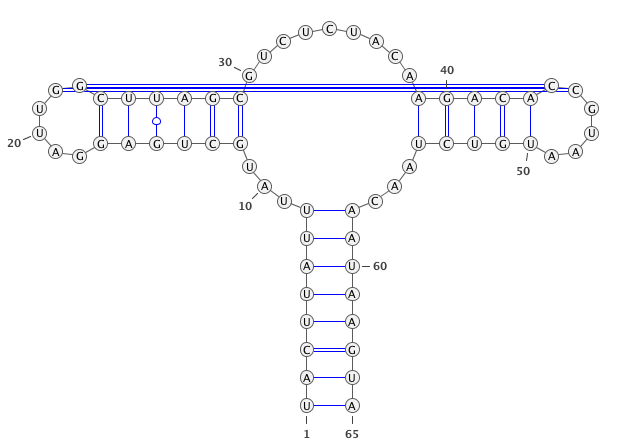
If
allow_guis False (be default is True) then GU pair is also possible.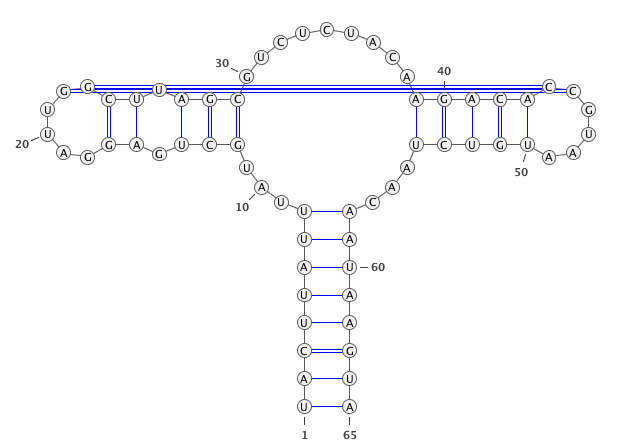
If you provide seq and secondary structure such as:
GgCcGGggG.GcggG.cc.u.aAUACAAuACCC.GaAA.GGGGAAUAaggCc.gGCc.gu......CU.......uugugcgGUuUUcaAgCccCCgGcCaCCcuuuu (((((((((....((.((............(((......)))......))))..(((.(.....................)))).......)))))))))........
gaps will be remove as well.
RNAalignment¶
- class rna_tools.tools.rna_alignment.rna_alignment.RNAalignment(fn='', fetch='')[source]¶
RNA alignment - adapter class around BioPython to do RNA alignment stuff
Usage (for more see IPython notebook https://github.com/mmagnus/rna-tools/blob/master/rna_tools/tools/rna_alignment/rna_alignment.ipynb)
>>> a = RNAalignment('test_data/RF00167.stockholm.sto') >>> print(a.tail()) >>> print(a.ss_cons)
- Parameters:
Read more:
and on the format itself
Warning
fetch requires urllib3
- copy_ss_cons_to_all_editing_sequence(seq_id, before, after)[source]¶
Change a sequence’s sec structure.
- Parameters:
seq_id – string, sequence id to change, eg:
AE009948.1/1094322-1094400before – string, character to change from, eg:
,after – string, character to change to, eg:
.
Warning
before and after has to be one character long
- describe()[source]¶
Describe the alignment.
> print(a.describe()) SingleLetterAlphabet() alignment with 13 rows and 82 columns
- find_core(ids=None)[source]¶
Find common core for ids.
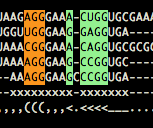
Fig. By core, we understand columns that have all homologous residues. The core is here marked by x.
- Parameters:
id – list, ids of seq in the alignment to use
- find_seq(seq, verbose=False)[source]¶
Find seq (also subsequences) and reverse in the alignment.
seq = "ggaucgcugaacccgaaaggggcgggggacccagaaauggggcgaaucucuuccgaaaggaagaguaggguuacuccuucgacccgagcccgucagcuaaccucgcaagcguccgaaggagaauc" hit = a.find_seq(seq, verbose=False) ggaucgcugaacccgaaaggggcgggggacccagaaauggggcgaaucucuuccgaaaggaagaguaggguuacuccuucgacccgagcccgucagcuaaccucgcaagcguccgaaggagaauc Match: AL939120.1/174742-174619 ID: AL939120.1/174742-174619 Name: AL939120.1 Description: AL939120.1/174742-174619 Number of features: 0 /start=174742 /end=174619 /accession=AL939120.1 Per letter annotation for: secondary_structure Seq('CCAGGUAAGUCGCC-G-C--ACCG---------------GUCA-----------...GGA', SingleLetterAlphabet()) GGAUCGCUGAACCCGAAAGGGGCGGGGGACCCAGAAAUGGGGCGAAUCUCUUCCGAAAGGAAGAGUAGGGUUACUCCUUCGACCCGAGCCCGUCAGCUAACCUCGCAAGCGUCCGAAGGAGAAUC
- find_seq_exact(seq, verbose=False)[source]¶
Find seq (also subsequences) and reverse in the alignment.
- Parameters:
seq – string, seq, seq is upper()
verbose – boolean, be verbose or not
- get_distances()[source]¶
Get distances (seq identity) all-vs-all.
With BioPython.
blastn:
Bad alphabet 'U' in sequence 'AE008922.1/409481-409568' at position '7'only for DNA?read more (also about matrix at <http://biopython.org/wiki/Phylo> and HTTP://biopython.org/DIST/docs/api/Bio.Phylo.TreeConstruction.DistanceCalculator-class.html
- get_ss_remove_gaps(seq, ss)[source]¶
- Parameters:
seq – string, sequence
ss – string, ss
UAU-AACAUAUAAUUUUGACAAUAUGG-GUCAUAA-GUUUCUACCGGAAUACC–GUAAAUAUUCU—GACUAUG-UAUA- (((.(.((((,,,(((((((_______.))))))).,,,,,,,,(((((((__.._____))))))…),,)))).)))).
- get_the_closest_seq_to_ref_seq(verbose=False)[source]¶
Example:
>>> a = RNAalignment("test_data/RF02221.stockholm.sto") >>> a.get_the_closest_seq_to_ref_seq() AF421314.1/431-344
- map_seq_on_align(seq_id, resis, v=True)[source]¶
- Parameters:
seqid – seq_id, ‘CP000721.1/2204691-2204775’
resis – list resis, [5,6]
maps:
[5, 6, 8] CAC-U CAC-U- CAC-U-UA [4, None, 6]
- map_seq_on_seq(seq_id, seq_id_target, resis, v=True)[source]¶
- Parameters:
seq_id – seq_id, ‘AAML04000013.1/228868-228953’
seq_id_target – seq_id of target, ‘CP000721.1/2204691-2204778’
resis – list resis, [5,6]
map:
[4, 5, 6] UAU-A UAU-AA UAU-AAC [5, 6, 7] CAC-U CAC-U- CAC-U-U [4, None, 5]
- remove_empty_columns(verbose=False)[source]¶
Remove empty columns in place.
Example:
>>> a = RNAalignment("test_data/zmp.stk") >>> print(a) SingleLetterAlphabet() alignment with 6 rows and 319 columns ---ACCUUGCGCGACUGGCGAAUCC-------------------...AAU CP001644.1/756294-756165 --GCUCUCGCGCGACUGGCGACUUUG------------------...GAA CU234118.1/352539-352459 UGAGUUUUCUGCGACUGACGGAUUAU------------------...CUG BAAV01000055.1/2897-2982 GCCCGUUCGCGUGACUGGCGCUAGU-------------------...CGA CP000927.1/5164264-5164343 -----GGGUCGUGACUGGCGAACA--------------------...--- zmp UCACCCCUGCGUGACUGGCGAUA---------------------...GUU AP009385.1/718103-718202 >>> a.remove_empty_columns() >>> print(a) SingleLetterAlphabet() alignment with 6 rows and 138 columns ---ACCUUGCGCGACUGGCGAAUCC-UGAAGCUGCUUUG-AGCG...AAU CP001644.1/756294-756165 --GCUCUCGCGCGACUGGCGACUUUG------------------...GAA CU234118.1/352539-352459 UGAGUUUUCUGCGACUGACGGAUUAU------------------...CUG BAAV01000055.1/2897-2982 GCCCGUUCGCGUGACUGGCGCUAGU-------------------...CGA CP000927.1/5164264-5164343 -----GGGUCGUGACUGGCGAACA--------G-----------...--- zmp UCACCCCUGCGUGACUGGCGAUA--------GAACCCUCGGGUU...GUU AP009385.1/718103-718202
go over all seq modifes self.nss_cons
- property ss_cons_std¶
- property ss_cons_with_pk¶
go over ss_cons and overwrite bp is there is pk (ss_cons_pk)
ss_cons: (((.(.((((,,,(((((((_______.))))))).,,,,,,,,(((((((__.._____))))))…),,)))).)))). ss_cons_pk: …………………..[[………………………….]]…………………… ss_cons_with_pk: (((.(.((((,,,(((((((___[[__.))))))).,,,,,,,,(((((((__.._]]__))))))…),,)))).)))).
“return ss_cons_with_pk: string, e.g. (((.(.((((,,,(((((((___[[__.))))
- property ss_cons_with_pk_std¶
- subset(ids, verbose=False)[source]¶
Get subset for ids:
# STOCKHOLM 1.0 #=GF WK Tetrahydrofolate_riboswitch
AAQK01002704.1/947-1059 -U-GC-AAAAUAGGUUUCCAUGC.. #=GC SS_cons .(.((.((—-((((((((((… #=GC RF .g.gc.aGAGUAGggugccgugc.. //
rna_alignment_get_species.py¶
This is an improved version of the script that uses the Rfam MySQL database online interface (thanks @akaped for this idea) (so you need to be connected to the Internet, of course). Redirect the output to the file.

Warning
This scripts needs mysql-connector-python-rf module to connect the Rfam MySQL server, so install it before using: pip install mysql-connector-python-rf.
Example:
$ rna_alignment_get_species.py RF00004.stockholm.stk
# STOCKHOLM 1.0
Sorex-araneus-(European-shrew) AUCGCU-UCU----CGGCC--UUU-U
Examples 2:
$ rna_alignment_get_species.py u5_rfam_u5only.stk --verbose
# STOCKHOLM 1.0
#=GF WK U5_spliceosomal_RNA
#=GF NC 39.90
#=GF RT The spliceosomal snRNAs of Caenorhabditis elegans.
#=GF TC 40.00
#=GF RN [3]
(...)
#=GF AC RF00020
#=GF SE Zwieb C, The uRNA database, PMID:9016512; PMID:18390578
#=GF GA 40.00
#=GF BM cmbuild -F CM SEED
#=GF TP Gene; snRNA; splicing;
Bos-taurus-(cattle) GAUC-GUAUAAAUCUUUCGCCUUUUACUAAAGA-UUUCCG----UGG-A--GA-G
Sorex-araneus-(European-shrew) GAUC-GUAUAAAUCUUUCGCCUUUUACUAAAGA-UUUCCG----UGG-A--GA-G
Ictidomys-tridecemlineatus-(thirteen-lined-ground- GAUC-GUAUAAAUCUUUCGCCUUUUACUAAAGA-UUUCCG----UGG-A--GA-G
Monodelphis-domestica-(gray-short-tailed-opossum) GAUC-GUAUAAAUCUUUCGCCUUUUACUAAAGA-UUUCCG----UGG-A--GA-G
Oryctolagus-cuniculus-(rabbit) GAUC-GUAUAAAUCUUUCGCCUUUUACUAAAGA-UUUCCG----UGG-A--GA-G
Cavia-porcellus-(domestic-guinea-pig) GAUC-GUAUAAAUCUUUCGCCUUUUACUAAAGA-UUUCCG----UGG-A--GA-G
Ochotona-princeps-(American-pika) GAUC-GUAUAAAUCUUUCGCCUUUUACUAAAGA-UUUCCG----UGG-A--GA-G
usage: rna_alignment_get_species.py [-h] [-v] [--debug] [--id-width ID_WIDTH]
[--evo-mapping EVO_MAPPING]
[--evo-mapping-default] [--one]
[--osfn OSFN] [--rfam]
alignment
- alignment¶
alignment
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- -v, --verbose¶
be verbose
- --debug¶
- --id-width <id_width>¶
define width of ids, trim species name when longer than this
- --evo-mapping <evo_mapping>¶
- --evo-mapping-default¶
- --one¶
- --osfn <osfn>¶
cache file
- --rfam¶
rna_alignment_calc_energy.py¶
Calculate energy (.cet) format:
UGGC-CCCUGCGCAA-GGAUGACA
(((..((((.....).))..))))
(((..(((((***)).))..))))
Examples:
$ rna_alignment_calc_energy.py --template alignments/u6-lower.cet alignments/u6-only-RemovedGapped.stk -v
--loop-upper guaa --loop-lower guaa
--loop-upper-cst '(..)' --loop-lower-cst '(..)'
calc-energy2.py --template u6atac-template.txt u6atac_u6only.sto -v
./calc-energy2.py --template alignments/u6-lower.cet --one alignments/u6-lower-stem-only.sto
Takes cet files (calc-energy-templets):
$ rna_alignment_calc_energy.py --template test_data/u6-lower.cet --one test_data/u6-only.stk -v # --loop-seq test_data/u6-only-loop-seq-u6-lower
N/A% (0 of 182) | | Elapsed Time: 0:00:00 ETA: --:--:--================================================================================
AB010698.1/46467-46488
(((..((((.....).))..))))
UGGC-CCCUGCGCAA-GGAUGACA
lower ------------------------------------
UGG ugcgca ACA
(((******)))
UGGugcgcaACA
(((((..))))) -10.64
upper ------------------------------------
UGGC-CCCUGCGCAA-GGAUGACA
CCC ugcgca AGG
CCCugcgcaAGG
(((((..))))) -9.6
id low_energy low_seq low_ss up_energy up_seq up_ss
0 AB010698.1/46467-46488 -10.64 UGGugcgcaACA (((((..))))) -9.6 CCCugcgcaAGG (((((..)))))
Done: u6-only-loop-seq-u6-lower
by parsing output from MC-Sym:
domains have 5451 elements.
10:47:16 up 141 days, 26 min, 0 users, load average: 1.45, 1.30, 1.56
Score: -999.000 GAACAUGGUUCUUGCCUUUUACCAGAACCAUCCGGGUGUUG
Total number of MB structures with 3 stems: 16041
(overlaps: 0, !energy: 335585)
</pre><P><H2>Sorting the structures...
<P></H2><pre></pre><H2><P><P><P>Filtered and Sorted solutions:<P><P><P></H2><pre>
</pre><H2><P><P><P><a HREF="http://biwww2.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/Software/MARNA/index.html" target="_blank">MARNA</a>-formatted:<P><P><P></H2><pre>
GAACAUGGUUCUUGCCUUUUACCAGAACCAUCCGGGUGUUG
((((((((((..))))))))))((((((((...)))))))) -33.20 ( -0.69)
(((((((((....)))))))))((((((((...)))))))) -33.17 ( -0.69)
((((((((((((((((...))))))))))))......)))) -32.40 ( +0.00)
Backtracking with 2 variables (stems):
domains have 5451 elements.
10:47:16 up 141 days, 26 min, 0 users, load average: 1.45, 1.30, 1.56
Score: -999.000 GAACAUGGUUCUUGCCUUUUACCAGAACCAUCCGGGUGUUG
Total number of MB structures with 2 stems: 9555
(overlaps: 0, !energy: 165582)
</pre><P><H2>Sorting the structures...
<P></H2><pre></pre><H2><P><P><P>Filtered and Sorted solutions:<P><P><P></H2><pre>
</pre><H2><P><P><P><a HREF="http://biwww2.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/Software/MARNA/index.html" target="_blank">MARNA</a>-formatted:<P><P><P></H2><pre>
GAACAUGGUUCUUGCCUUUUACCAGAACCAUCCGGGUGUUG
((((((((((..))))))))))((((((((...)))))))) -33.20 ( -0.69)
(((((((((....)))))))))((((((((...)))))))) -33.17 ( -0.69)
((((((((((((((((...))))))))))))......)))) -32.40 ( +0.00)
usage: rna_alignment_calc_energy.py [-h] [--debug] [--one] [--method METHOD]
[--csv CSV] [--loop-seq]
[--template TEMPLATE] [--flanks FLANKS]
[-v]
alignment
- alignment¶
an alignment in the Stockholm format
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- --debug¶
- --one¶
one only for the first seq
- --method <method>¶
mcfold or rnastructure_CycleFold
- --csv <csv>¶
- --loop-seq¶
- --template <template>¶
- --flanks <flanks>¶
GC be default
- -v, --verbose¶
rna_align_get_ss_from_fasta.py¶
Input as a file:
>ade
GCU-U-CAUAUAAUCCUAAUGAUAUGG-UUUGGGA-GUUUCUACCAAGAG-CC--UUAAA-CUCUU---GAUUAUG-AAGU-
(((.(.((((,,,(((((((_______.))))))).,,,,,,,,(((((((__.._____))))))...),,)))).)))).
to get:
>ade
GCUUCAUAUAAUCCUAAUGAUAUGGUUUGGGAGUUUCUACCAAGAGCCUUAAACUCUUGAUUAUGAAGU
((((((((...(((((((.......)))))))........((((((.......))))))..))))))))
usage: rna_align_get_ss_from_fasta.py [-h] file
- file¶
subsection of an alignment
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
rna_align_get_ss_from_stk.py¶
Process an alignment in the Stockholm format to get sequences and secondary structures:
Example:
$ rna_align_get_ss_from_stk.py aligns/gmp_RF01786.stockholm_p75_pk.sto
AAOX01000007.1/31274-31356
AAGAAUAUAGAACACUGUGAUGAGCGGUUUUUAUUUGCACUUUAAACCGCUUGGAGUGACUAGUGCAGCCGGCCAAUGAUCUA
.(((.(((.(..(((......((((((((...............))))))))...)))...............).))).))).
CP000724.1/3560727-3560809
AAAAAUGUAGAGCAAAUGAACUGCAGGUAUACAUGGACGCCUUAAACUGCAGGGAUGUAGUGGCGUAACCGACUAACAAUAUU
((.(.(((((.(((......((((((.(......[[...[....).))))))...)))...]...]..]...))).)).).))
AACY023761929.1/1009-1091
AUAAUUUGGUGGGCGUUGAUGUGCCCUUUGUAUCUGGUCGCUUGAGGGGUACGGAGCCAAUAGCGAAACCGCCGCCGUCAUAG
.((...((((((((......((((((((.......[.[......))))))))...)))......]...]...)))))...)).
usage: rna_align_get_ss_from_stk.py [-h] file
- file¶
subsection of an alignment
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
rna_align_distance_to_seq.py¶
Calculate
“Process an alignment in the Stockholm format to get sequences and secondary structures:
Example:
$ rna_align_distance_to_seq.py test_data/gmp_ref.sto test_data/gmp_ref_distance.csv
distance id
0 1.00 gmp
1 0.69 AE000513.1/1919839-1919923
2 0.73 BA000004.3/387918-388001
3 0.69 ABFD02000011.1/154500-154585
4 0.73 AE015927.1/474745-474827
5 0.75 AAWL01000006.1
6 0.72 AM180355.1
7 0.72 CP001116.1/102374-102457
8 0.65 AJ965256.1/1260708-1260792
seq
0 -----GCGCGGAAAC-AAUGAUGAAU--GGG-UUUA-AAUUGGGC-...
1 CUGUCGAAGAGACGC-GAUGAAUCCC--GCC-CUGUAAUUCGGGC-...
2 AAUCAAUAGGGAAGC-AACGAAGCAU--AGC-CUUU-AUAUGGAC-...
3 AAAUAUUAUAGAGAU-GUUGAAGUAU--AUU-CUAUUA-UUGGGC-...
4 AUUUUAAGAGGAAAU-UUUGAACUAU--AUA-CUU--AUUUGGGC-...
5 --UGCAA-UGGGUGU-GAUGAAGUCC--GGA-CAGUAAUGUGGGC-...
6 AAUAUUU-UAGAAAC-UGAGAAGUAU--AUC-UUAUUA-UUGGGC-...
7 AUAACGGCACGAAGC-AAUGAAAUGU--UCG-AUGU-AACCGGGC-...
8 AAAUUAAGGGGAAGC-GUUGAGCCGC--UAC-CCAU-AUGUGGUUC...
ss:
0 (((((((((((.(((.......((((..(((.(................
1 (((((((((((.(((.......((((..(((.(................
2 (((((((((((.(((.......((((..(((.(................
3 (((((((((((.(((.......((((..(((.(................
4 (((((((((((.(((.......((((..(((.(................
5 (((((((((((.(((.......((((..(((.(................
6 (((((((((((.(((.......((((..(((.(................
7 (((((((((((.(((.......((((..(((.(................
8 (((((((((((.(((.......((((..(((.(................
usage: rna_align_distance_to_seq.py [-h] file output
- file¶
an alignment in the Stokholm format, the first seq will be used to calculate distance to (#TODO pick any seq)
- output¶
csv pandas file
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
rna_align_foldability.py¶
Calculate statistics of foldability on an alignment.
The tool uses ENTRANA [1] to calculate, what the authors called, foldability (column: “foldability”) of a given sequence into a given secondary structure.
Next, MC-Fold [2] is executed to calculate free energy (column: “mcsym”) on the sequence and the secondary structure obtained based on the alignment. The secondary structure is used as constraints.
The third used program is RNAfold from the Vienna package [3]. Also, in this case the secondary structure obtained with rna-tools from the RNA alignment is used as constraints, columns: “mfe” (minimum free energy), “mfess” (secondary structure for minimum free energy state), “cfe” (minimum free energy of centroid), “cfess” (secondary structure for centroid, “diversity” (ensemble diversity), “efe” (free energy of the thermodynamic ensemble), “efess” (secondary structure for the thermodynamic ensemble), “freq” (frequency of mfe structure in ensemble). RNAfold is also executed in with “–enforceConstraint” where the constraints are enforced. This run gives analogous values as the default RNAfold, to all RNAfold column “_enforce” is added.
The tool is able to calculate the distance Levenshtein (the difference between the two sequences)(column: “distance”) from the target sequence and all sequence in the alignment to test if there is a bias in the accuracy towards the most similar sequences.
Another tool used from the Vienna package is RNAeval. The tool calculates free energy for a given sequence and secondary structure.
The accuracy is expressed as the median of core RMSD of 10% the lowest core RMSD models for the given sequences.
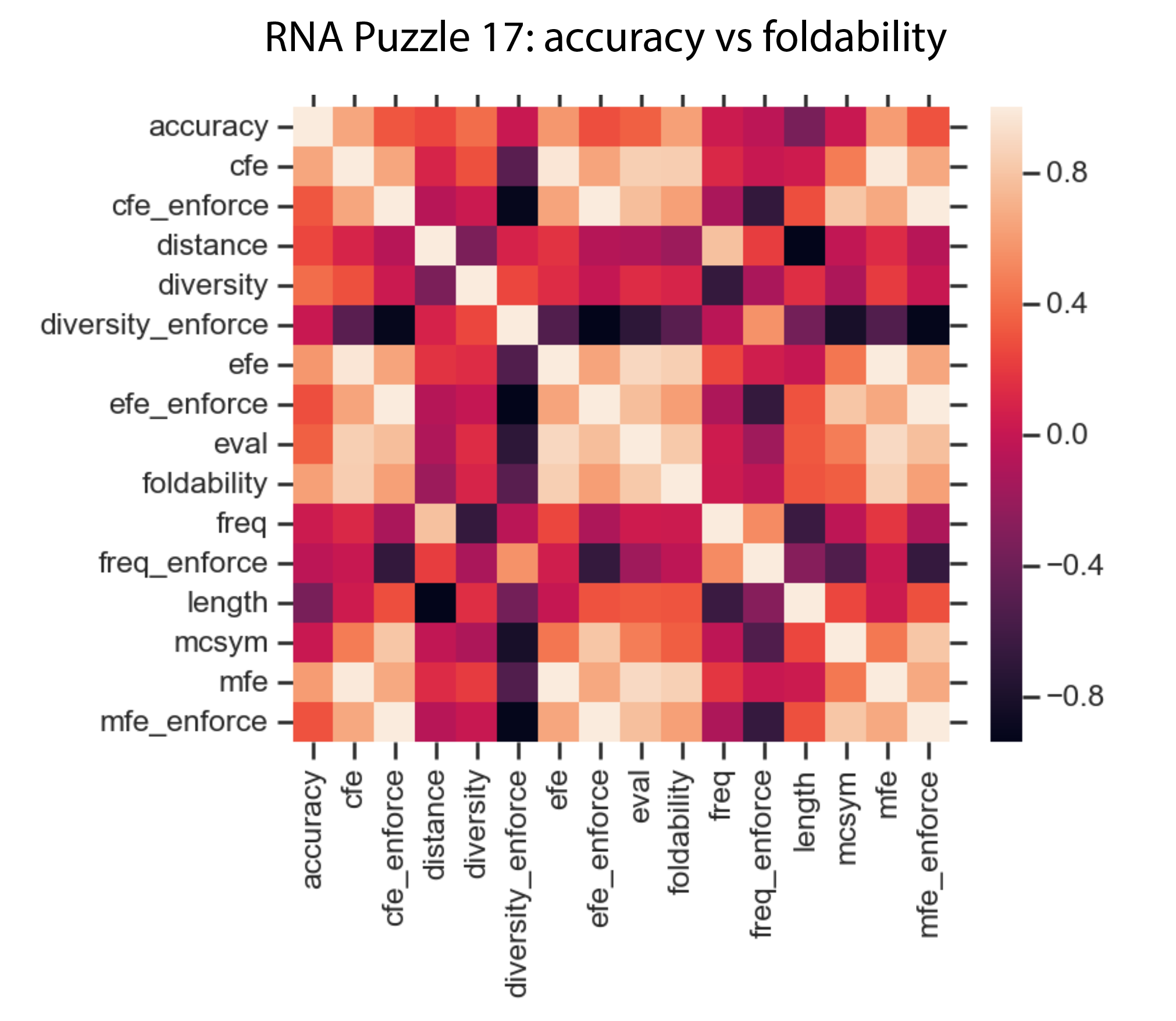
The correlations:
accuracy 1.000000
cfe 0.653813
foldability 0.622038
mfe 0.607340
efe 0.585077
diversity 0.404350
eval 0.349499
cfe_enforce 0.311744
mfe_enforce 0.302973
efe_enforce 0.280929
distance 0.256870
freq 0.037037
diversity_enforce 0.018429
mcsym 0.017533
freq_enforce -0.037991
length -0.340809
The data:
We tested correlations between the above-mentioned statistics, and the highest correlation, 0.65 () was achieved to the centroid free energy calculated with RNAFold, which suggests that to some extent this metric could be used to pick sequence from the alignment to pick sequences that are more likely to fold.
However, this needs further investigation and the detailed analysis an all cases and more folded sequences.
Su C, Weir JD, Zhang F, Yan H, Wu T. ENTRNA: a framework to predict RNA foldability. BMC Bioinformatics. BioMed Central 2019
Parisien M, Major F. The MC-Fold and MC-Sym pipeline infers RNA structure from sequence data. Nature 2008;452:51-5
Lorenz R, Bernhart SH, Honer Zu Siederdissen C, Tafer H, Flamm C, Stadler PF, et al. ViennaRNA Package 2.0. Algorithms Mol Biol. BioMed Central; 2011;6:26-14.
Example:
$ python rna_align_foldability.py test_data/gmp_ref.sto test_data/gmp_foldability.csv
cfess_enforce distance diversity
0 ((((((.(((......(((((((((..............)))))))... 1.00 3.96
1 (((.(((((((..((......(((((.(((((.......)))....... 0.69 5.56
2 0.73 3.84
3 0.69 5.92
4 (((....((((.((((((...((((((((...............))... 0.73 7.49
5 ((((.(((.(((..((..((((((((.................)))... 0.75 7.92
6 .(((((((((.((((.....(((((((((...............))... 0.72 5.83
7 0.72 7.35
8 ...((((((((.(((......((((((.((....(((...)))..)... 0.65 4.86
diversity_enforce efe efe_enforce
0 2.89 -14.77 -13.75
1 3.70 -19.52 -18.25
2 0.00 -15.41 0.00
3 0.00 -13.55 0.00
4 2.46 -8.58 -6.91
5 6.37 -20.72 -20.08
6 2.92 -11.87 -11.38
7 0.00 -14.59 0.00
8 3.83 -21.16 -20.64
efess
0 ((((((..........(((((((((..............)))))))...
1 {{..(((((((..((......(((((.(({((.......}}).......
2 .......((((.(((..(...(((((((((..............))...
3 .....((((((.(((.....(((((((((.......{{...,}..,...
4 .......{(((.,{{{{,...((((((((...............))...
5 {(((.(((.(((..((..((((((((,{{...,.....)}}..)))...
6 .(((((((((.((((.....(((((((((...............))...
7 .....{,.{{{.(((......((((((((((..........,.}))...
8 ...{(((((((.(((......((((((.((....(((...)))..)...
... length mcsym
0 ... 75.0 -39.73
1 ... 85.0 -37.89
2 ... 84.0 -35.40
3 ... 86.0 -36.11
4 ... 83.0 -37.37
5 ... 80.0 -43.59
6 ... 84.0 -42.95
7 ... 84.0 -36.55
8 ... 85.0 -43.58
mcsym comment
0 energy best dynamics programming
1 BP energy
2 BP energy
3 BP energy
4 energy best dynamics programming
5 energy best dynamics programming
6 energy best dynamics programming
7 BP energy
8 energy best dynamics programming
mcsym ss mfe mfe_enforce
0 ((((((.(((......((((((((................))))))... -13.9 -12.9
1 (((.(((((((..((......(((((.((.................... -18.0 -17.3
2 ....(..((((.(((......((((((((................)... -14.0 0.0
3 .(...((((((.(((......((((((((.................... -12.0 0.0
4 (((....((((.(((......((((((((...............))... -7.2 -6.1
5 ((((.(((.(((......((((((((.................)))... -18.6 -18.6
6 .(((((((((.(((......((((((((.................)... -10.5 -10.5
7 ...(.((.(((.(((......((((((((................)... -12.8 0.0
8 ...((((((((.(((......((((((.(.................... -19.8 -19.8
mfess
0 ((((((..........(((((((((..............)))))))...
1 ((..(((((((..((......(((((.(((((.......))).......
2 .......((((.(((......(((((((((..............))...
3 .....((((((.(((.....(((((((((....................
4 .....................((((((((...............))...
5 ((((.(((.(((..((..(((((((((((.........)))..)))...
6 .(((((((((.((((.....(((((((((...............))...
7 .....((.(((.(((......((((((((((............)))...
8 ...((((((((.(((......((((((.((....(((...)))..)...
mfess_enforce
0 ((((((.(((......(((((((((..............)))))))...
1 (((.(((((((..((......(((((.(((((.......))).......
2 error
3 error
4 (((....((((.((((((...((((((((...............))...
5 ((((.(((.(((..((..(((((((((((.........)))..)))...
6 .(((((((((.((((.....(((((((((...............))...
7 error
8 ...((((((((.(((......((((((.((....(((...)))..)...
seq
0 GCGCGGAAACAAUGAUGAAUGGGUUUAAAUUGGGCACUUGACUCAU...
1 CUGUCGAAGAGACGCGAUGAAUCCCGCCCUGUAAUUCGGGCACCUC...
2 AAUCAAUAGGGAAGCAACGAAGCAUAGCCUUUAUAUGGACACUUGG...
3 AAAUAUUAUAGAGAUGUUGAAGUAUAUUCUAUUAUUGGGCACCUUA...
4 AUUUUAAGAGGAAAUUUUGAACUAUAUACUUAUUUGGGCACUUUGU...
5 UGCAAUGGGUGUGAUGAAGUCCGGACAGUAAUGUGGGCACUUAGUC...
6 AAUAUUUUAGAAACUGAGAAGUAUAUCUUAUUAUUGGGCAUCUGGA...
7 AUAACGGCACGAAGCAAUGAAAUGUUCGAUGUAACCGGGCACCUAU...
8 AAAUUAAGGGGAAGCGUUGAGCCGCUACCCAUAUGUGGUUCACUCG...
ss
0 ((((((.(((......((((((((................))))))...
1 (((.(((((((..((......(((((.((....................
2 ....(..((((.(((......((((((((................)...
3 .(...((((((.(((......((((((((....................
4 (((....((((.(((......((((((((...............))...
5 ((((.(((.(((......((((((((.................)))...
6 .(((((((((.(((......((((((((.................)...
7 ...(.((.(((.(((......((((((((................)...
8 ...((((((((.(((......((((((.(....................
[9 rows x 26 columns]
usage: rna_align_foldability.py [-h] [--all-stars] [--dev] [--skip-mcfold]
[-v]
file output
- file¶
an alignment in the Stokholm format, the first seq will be used to calculate distance to (#TODO pick any seq)
- output¶
csv pandas file
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- --all-stars¶
this takes usully super long
- --dev¶
- --skip-mcfold¶
- -v, --verbose¶
be verbose
Random assignment of nucleotides¶
random_assignment_of_nucleotides.py¶
random_assignment_of_nucleotides.py - Random assignment of nucleotides for non-typical characters in the sequence alignment (arg –alignfn or fasta file with sequneces (arg –seqfn)
R = G A (purine)
Y = U C (pyrimidine)
K = G U (keto)
M = A C (amino)
S = G C (strong bonds)
W = A U (weak bonds)
B = G U C (all but A)
D = G A U (all but C)
H = A C U (all but G)
V = G C A (all but T)
N = A G C U (any)
author: A. Zyla - azyla
Warning
Tested only on fasta files! and requires Biopython (tested with v1.68)
usage: random_assignment_of_nucleotides.py [-h] [-v] [--alignfn ALIGNFN]
[--seqfn SEQFN] [--outfn OUTFN]
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- -v, --verbose¶
increase output verbosity
- --alignfn <alignfn>¶
alignment in the Fasta format
- --seqfn <seqfn>¶
sequences in the Fasta format
- --outfn <outfn>¶
output aln file (default: alnfn .fasta -> _out.fasta)
random_assignment_of_nucleotides.py - Random assignment of nucleotides for non-typical characters in the sequence alignment (arg –alignfn or fasta file with sequneces (arg –seqfn)
R = G A (purine)
Y = U C (pyrimidine)
K = G U (keto)
M = A C (amino)
S = G C (strong bonds)
W = A U (weak bonds)
B = G U C (all but A)
D = G A U (all but C)
H = A C U (all but G)
V = G C A (all but T)
N = A G C U (any)
author: A. Zyla - azyla
Warning
Tested only on fasta files! and requires Biopython (tested with v1.68)
- rna_tools.tools.rna_alignment.random_assignment_of_nucleotides.get_align(alignfn)[source]¶
- Get seq from an alignment with gaps.
- Args:
alignfn (str): a path to an alignment
- Usage::
>>> get_align('test_data/aln1.fasta') SingleLetterAlphabet() alignment with 2 rows and 13 columns AGGGGGACAGNYU 1 CYGA------CGG 2
- obj1’, description=’obj1’, dbxrefs=[]), id=’<unknown id>’, name=’<unknown name>’, description=’<unknown description>’, dbxrefs=[])
- Returns:
alignment
- rna_tools.tools.rna_alignment.random_assignment_of_nucleotides.get_sequences(seqfn)[source]¶
Get seq from an fasta file. :param seqfn: a path to a fasta file :type seqfn: str
- Usage::
>>> get_align('test_data/fasta.fasta')
- Returns:
[SeqRecord(seq=Seq(‘GGGYYGCCNRW’, SingleLetterAlphabet()), id=’1’, name=’1’, description=’1’, dbxrefs=[]), SeqRecord(seq=Seq(‘GGRGYYGCCUURWAA’, SingleLetterAlphabet()), id=’1’, name=’1’, description=’1’, dbxrefs=[])]
- rna_tools.tools.rna_alignment.random_assignment_of_nucleotides.write_align(align, outfn)[source]¶
Write cleaned alignment with Biopython. :param align: a cleaned alignment :type align: obj :param outfn: a path to a new alignment file :type outfn: str
- Returns:
writes to a file in fasta format
- Return type:
none
- rna_tools.tools.rna_alignment.random_assignment_of_nucleotides.write_seq(seqfn, outfn)[source]¶
Write cleaned alignment with Biopython. :param align: a cleaned alignment :type align: obj :param outfn: a path to a new alignment file :type outfn: str
- Returns:
writes to a file in fasta format
- Return type:
none
CMAlign¶
- class rna_tools.tools.rna_alignment.rna_alignment.CMAlign(outputfn=None)[source]¶
CMAalign class around cmalign (of Inferal).
cmalign - aligns the RNA sequences in <seqfile> to the covariance model (CM) in <cmfile>. The new alignment is output to stdout in Stockholm format.
Example:
cma = ra.CMAlign() cma.run_cmalign("ade_seq.fa", "RF00167.cm") seq = cma.get_seq() print 'cma hit ', seq print 'seq ', a.align_seq(seq) print 'a.rf ', a.rf cmd cmalign -g RF00167.cm ade_seq.fa # STOCKHOLM 1.0 #=GF AU Infernal 1.1.2 ade ----------------CGCUUCAUAUAAUCCUAAUGAUAUGGUUUGGGAGUUUCUACCAAGAG-CCUUAAA-CUCUUGAUUAUGAAGUGA------------ #=GR ade PP ................99*********************************************.*******.***************999............ #=GC SS_cons :::::::::::::::::((((((((,,,<<<<<<<_______>>>>>>>,,,,,,,,<<<<<<<_______>>>>>>>,,)))))))):::::::::::::: #=GC RF aaaaaauaaaaaaaauucccuCgUAUAAucccgggAAUAUGGcccgggaGUUUCUACCaggcagCCGUAAAcugccuGACUAcGagggaaauuuuuuuuuuu // cma hit ----------------CGCUUCAUAUAAUCCUAAUGAUAUGGUUUGGGAGUUUCUACCAAGAG-CCUUAAA-CUCUUGAUUAUGAAGUGA------------ seq ----------------CGCU-U-CAUAUAAUCCUAAUGAUAUGG-UUUGGGA-GUUUCUACCAAGAG-CC--UUAAA-CUCUU---GAUUAUG-AAGUGA------------- a.rf aaaaaauaaaaaaaauuccc.u.CgUAUAAucccgggAAUAUGG.cccggga.GUUUCUACCaggcagCC..GUAAAcugccu...GACUAcG.agggaaauuuuuuuuuuu.
Install http://eddylab.org/infernal/
Cite: Nawrocki and S. R. Eddy, Infernal 1.1: 100-fold faster RNA homology searches, Bioinformatics 29:2933-2935 (2013).
- run_cmalign(seq, cm, verbose=True)[source]¶
Run cmalign and process the result.
- Parameters:
seq – seq string
cm – cm fn
Run:
$ cmalign RF01831.cm 4lvv.seq # STOCKHOLM 1.0 #=GF AU Infernal 1.1.2 4lvv -GGAGAGUA-GAUGAUUCGCGUUAAGUGUGUGUGA-AUGGGAUGUCG-UCACACAACGAAGC---GAGA---GCGCGGUGAAUCAUU-GCAUCCGCUCCA #=GR 4lvv PP .********.******************9999998.***********.8999999******8...5555...8**************.************ #=GC SS_cons (((((----(((((((((((,,,,,<<-<<<<<<<<___________>>>>>>>>>>,,,<<<<______>>>>,,,)))))))))))-------))))) #=GC RF ggcaGAGUAGggugccgugcGUuAAGUGccggcgggAcGGGgaGUUGcccgccggACGAAgggcaaaauugcccGCGguacggcaccCGCAUcCgCugcc //
Warning
requires cmalign to be set in your shell
RChie¶
- class rna_tools.tools.rna_alignment.rna_alignment.RChie[source]¶
RChie - plotting arc diagrams of RNA secondary structures.
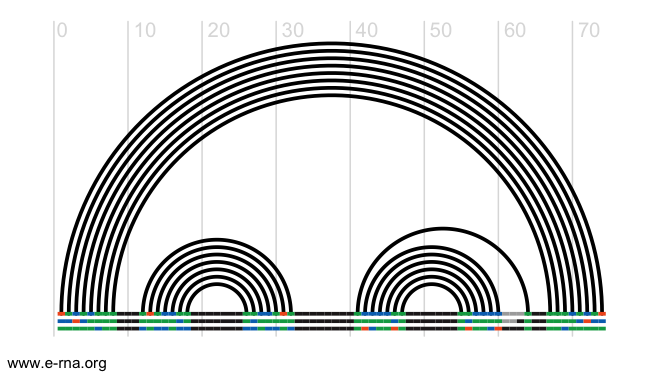
The offline version of R-chie, which requires first installing R4RNA is available here, or clone our git repository here How to install it:
Ensure R is installed already, or download it freely from http://www.r-project.org/
Download the R4RNA (https://github.com/jujubix/r-chie), open R and install the package:
install.packages("<path_to_file>/R4RNA", repos = NULL, type="source") # Install the optparse and RColorBrewer install.packages('optparse') install.packages('RColorBrewer')
Go to rna_tools/rna_tools_config_local.py and set RCHIE_PATH to the folder with RChie, e.g.
"/home/magnus/work/opt/r-chie/".
To test if Rchie works on your machine (from rna_align folder):
<path to your rchie>/rchie.R --msafile test_data/rchie_test_files/fasta.txt test_data/rchie_test_files/helix.txt
you should have rchie.png file in the folder.
More at http://www.e-rna.org/r-chie/download.cgi
Cite: Daniel Lai, Jeff R. Proctor, Jing Yun A. Zhu, and Irmtraud M. Meyer (2012) R-chie: a web server and R package for visualizing RNA secondary structures. Nucleic Acids Research, first published online March 19, 2012. doi:10.1093/nar/gks241
Renumber a pdb file according to alignment¶
renum_to_aln.py¶
renum_pdb_to_aln.py - renumber a pdb file based on the alignment.
author: A. Zyla under supervision of mmagnus
Warning
works only for single chain! and requires Biopython (tested with v1.68)
usage: renum_to_aln.py [-h] [-v] [--residue_index_start RESIDUE_INDEX_START]
[--outfn OUTFN]
seqid alignfn pdbfn
- seqid¶
seq id in the alignemnt
- alignfn¶
alignemnt in the Fasta format
- pdbfn¶
pdb file
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- -v, --verbose¶
increase output verbosity
- --residue_index_start <residue_index_start>¶
renumber starting number (default: 1)
- --outfn <outfn>¶
output pdb file (default: pdbfn .pdb -> _out.pdb)
renum_pdb_to_aln.py - renumber a pdb file based on the alignment.
author: A. Zyla under supervision of mmagnus
Warning
works only for single chain! and requires Biopython (tested with v1.68)
- rna_tools.tools.renum_pdb_to_aln.renum_pdb_to_aln.get_seq(alignfn, seqid)[source]¶
Get seq from an alignment with gaps.
Usage:
>>> get_seq('test_data/ALN_OBJ1_OBJ2.fa', 'obj1') SeqRecord(seq=SeqRecord(seq=Seq('GUUCAG-------------------UGAC-', SingleLetterAlphabet()), id='obj1', name='obj1', description='obj1', dbxrefs=[]), id='<unknown id>', name='<unknown name>', description='<unknown description>', dbxrefs=[])
- Returns:
SeqRecord
- rna_tools.tools.renum_pdb_to_aln.renum_pdb_to_aln.open_pdb(pdbfn)[source]¶
Open pdb with Biopython.
- Parameters:
pdbfn (str) – a path to a pdb structure
- Returns:
with a pdb structure
- Return type:
PDB Biopython object
Root Mean Square Deviation (RMSD)¶
rna_calc_rmsd¶
rna_calc_rmsd¶
rna_calc_rmsd.py - calculate RMSDs of structures to the target
If you still have problem with various number of atoms, check out this issue: get_rnapuzzle_ready: how to deal with `Alternate location indicator (https://github.com/mmagnus/rna-pdb-tools/issues/30).
The program is using (https://github.com/charnley/rmsd).
Example #1:
$ rna_calc_rmsd.py -t 6_0_solution_4GXY_rpr.pdb --model-selection=A:1-17+24-110+115-168 *.pdb
rmsd_calc_rmsd_to_target
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
method: all-atom-built-in
# of models: 35
6_0_solution_4GXY_rpr.pdb 0.0 3409
6_Blanchet_1_rpr.pdb 22.31 3409
6_Blanchet_2_rpr.pdb 21.76 3409
6_Blanchet_3_rpr.pdb 21.32 3409
6_Blanchet_4_rpr.pdb 22.22 3409
6_Blanchet_5_rpr.pdb 24.17 3409
6_Blanchet_6_rpr.pdb 23.28 3409
6_Blanchet_7_rpr.pdb 22.26 3409
6_Bujnicki_1_rpr.pdb 36.95 3409
6_Bujnicki_2_rpr.pdb 30.9 3409
6_Bujnicki_3_rpr.pdb 32.1 3409
6_Bujnicki_4_rpr.pdb 32.04 3409
...
Example #2:
time rmsd_calc_to_target.py
-t 5k7c_clean_onechain_renumber_as_puzzle_srr.pdb
--target-selection A:1-48+52-63
--model-selection A:1-48+52-63
--target-ignore-selection A/57/O2\'
clusters/*_AA.pdb
rmsd_calc_rmsd_to_target
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
target_selection: A:1-48+52-63
model_selection: A:1-48+52-63
target_ignore_selection: A/57/O2'
model_ignore_selection:
# of models: 801
fn,rmsd_all
pistol_thrs0.50A_clust01-000001_AA.pdb,7.596
pistol_thrs0.50A_clust02-000001_AA.pdb,7.766
pistol_thrs0.50A_clust03-000001_AA.pdb,18.171
[..]
pistol_thrs0.50A_clust799-000001_AA.pdb,5.356
pistol_thrs0.50A_clust800-000001_AA.pdb,15.282
pistol_thrs0.50A_clust801-000001_AA.pdb,16.339
# of atoms used: 1237
csv was created! rmsds.csv
rmsd_calc_to_target.py -t 5k7c_clean_onechain_renumber_as_puzzle_srr.pdb
37.93s user 1.07s system 87% cpu 44.650 total
Works also for multiple chains:
rna_calc_rmsd.py –model-selection=’A:52+53+59+60+61+80+B:21+22+23’ –target-selection=’A:52+53+59+60+61+80+B:21+22+23’ -t yC_5LJ3_U2U6_core_mdrFx_onlyTriplex_rpr.pdb yC_5LJ3_U2U6_core_mdrFx_addh_MD_1_rpr_rchain.pdb
usage: rna_calc_rmsd [-h] -t TARGET_FN [--ignore-files IGNORE_FILES]
[--target-selection TARGET_SELECTION]
[--target-ignore-selection TARGET_IGNORE_SELECTION]
[--model-selection MODEL_SELECTION]
[--model-ignore-selection MODEL_IGNORE_SELECTION]
[-m METHOD] [-o RMSDS_FN] [-v] [-pr] [-sr] [-pp]
[--way WAY] [--name-rmsd-column NAME_RMSD_COLUMN]
[--target-column-name]
files [files ...]
- files¶
files
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- -t <target_fn>, --target-fn <target_fn>¶
pdb file
- --ignore-files <ignore_files>¶
files to be ingored, .e.g, ‘solution’
- --target-selection <target_selection>¶
selection, e.g. A:10-16+20, where #16 residue is included
- --target-ignore-selection <target_ignore_selection>¶
A/10/O2’
- --model-selection <model_selection>¶
selection, e.g. A:10-16+20, where #16 residue is included
- --model-ignore-selection <model_ignore_selection>¶
A/10/O2’
- -m <method>, --method <method>¶
align, fit
- -o <rmsds_fn>, --rmsds-fn <rmsds_fn>¶
ouput, matrix
- -v, --verbose¶
verbose
- -pr, --print-results¶
- -sr, --sort-results¶
- -pp, --print-progress¶
- --way <way>¶
R|c1p = C1’ backbone = P OP1 OP2 O5’ C5’ C4’ C3’ O3’ po = P OP1 OP2 no-backbone = all - po bases, backbone+sugar, sugar pooo = P OP1 OP2 O5’ alpha = P OP1 OP2 O5’ C5’
- --name-rmsd-column <name_rmsd_column>¶
default: fn,rmsd, with this cols will be fn,<name-rmsd-column>
- --target-column-name¶
rna_calc_rmsd.py - calculate RMSDs of structures to the target
If you still have problem with various number of atoms, check out this issue: get_rnapuzzle_ready: how to deal with `Alternate location indicator (https://github.com/mmagnus/rna-pdb-tools/issues/30).
The program is using (https://github.com/charnley/rmsd).
Example #1:
$ rna_calc_rmsd.py -t 6_0_solution_4GXY_rpr.pdb --model-selection=A:1-17+24-110+115-168 *.pdb
rmsd_calc_rmsd_to_target
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
method: all-atom-built-in
# of models: 35
6_0_solution_4GXY_rpr.pdb 0.0 3409
6_Blanchet_1_rpr.pdb 22.31 3409
6_Blanchet_2_rpr.pdb 21.76 3409
6_Blanchet_3_rpr.pdb 21.32 3409
6_Blanchet_4_rpr.pdb 22.22 3409
6_Blanchet_5_rpr.pdb 24.17 3409
6_Blanchet_6_rpr.pdb 23.28 3409
6_Blanchet_7_rpr.pdb 22.26 3409
6_Bujnicki_1_rpr.pdb 36.95 3409
6_Bujnicki_2_rpr.pdb 30.9 3409
6_Bujnicki_3_rpr.pdb 32.1 3409
6_Bujnicki_4_rpr.pdb 32.04 3409
...
Example #2:
time rmsd_calc_to_target.py
-t 5k7c_clean_onechain_renumber_as_puzzle_srr.pdb
--target-selection A:1-48+52-63
--model-selection A:1-48+52-63
--target-ignore-selection A/57/O2\'
clusters/*_AA.pdb
rmsd_calc_rmsd_to_target
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
target_selection: A:1-48+52-63
model_selection: A:1-48+52-63
target_ignore_selection: A/57/O2'
model_ignore_selection:
# of models: 801
fn,rmsd_all
pistol_thrs0.50A_clust01-000001_AA.pdb,7.596
pistol_thrs0.50A_clust02-000001_AA.pdb,7.766
pistol_thrs0.50A_clust03-000001_AA.pdb,18.171
[..]
pistol_thrs0.50A_clust799-000001_AA.pdb,5.356
pistol_thrs0.50A_clust800-000001_AA.pdb,15.282
pistol_thrs0.50A_clust801-000001_AA.pdb,16.339
# of atoms used: 1237
csv was created! rmsds.csv
rmsd_calc_to_target.py -t 5k7c_clean_onechain_renumber_as_puzzle_srr.pdb
37.93s user 1.07s system 87% cpu 44.650 total
Works also for multiple chains:
rna_calc_rmsd.py –model-selection=’A:52+53+59+60+61+80+B:21+22+23’ –target-selection=’A:52+53+59+60+61+80+B:21+22+23’ -t yC_5LJ3_U2U6_core_mdrFx_onlyTriplex_rpr.pdb yC_5LJ3_U2U6_core_mdrFx_addh_MD_1_rpr_rchain.pdb
- rna_tools.tools.rna_calc_rmsd.rna_calc_rmsd.calc_rmsd(a, b, target_selection, target_ignore_selection, model_selection, model_ignore_selection, way, verbose)[source]¶
Calculate RMSD between two XYZ files
by: Jimmy Charnley Kromann <jimmy@charnley.dk> and Lars Andersen Bratholm <larsbratholm@gmail.com> project: https://github.com/charnley/rmsd license: https://github.com/charnley/rmsd/blob/master/LICENSE
a is model b is target
- Params:
a = filename of structure a
- Params:
b = filename of structure b
- Returns:
rmsd, number of atoms
- rna_tools.tools.rna_calc_rmsd.rna_calc_rmsd.calc_rmsd_pymol(pdb1, pdb2, method)[source]¶
Calculate rmsd using PyMOL. Two methods are available: align and fit
See:
Align can return a list with 7 items:
RMSD after refinement
Number of aligned atoms after refinement
Number of refinement cycles
RMSD before refinement
Number of aligned atoms before refinement
Raw alignment score
Number of residues aligned
in this version of function, the function returns RMSD before refinement.
Install on OSX:
brew install brewsci/bio/pymolor getIf you have a problem:
Match-Error: unable to open matrix file '/opt/local/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/lib/python2.7/site-packages/data/pymol/matrices/BLOSUM62'.
then find BLOSUM62, e.g.:
mdfind -name BLOSUM62 | grep pymol /Users/magnus/miniconda2/envs/py37/lib/python3.7/site-packages/pymol/pymol_path/data/pymol/matrices/BLOSUM62 /usr/local/Cellar/pymol/2.4.0_3/libexec/lib/python3.9/site-packages/pymol/pymol_path/data/pymol/matrices/BLOSUM62 /Users/magnus/miniconda2/pkgs/pymol-2.4.2-py37h06d7bae_0/share/pymol/data/pymol/matrices/BLOSUM62 /Users/magnus/work/opt/pymol-open-source/data/pymol/matrices/BLOSUM62
and then define
PYMOL_DATAin your .bashrc/.zshrc, e.g.:export PYMOL_DATA="/Users/magnus/work/opt/pymol-open-source/data/pymol"
- rna_tools.tools.rna_calc_rmsd.rna_calc_rmsd.get_rna_models_from_dir(files)[source]¶
- Parameters:
models – a list of filenames
Example of the list:
['test_data/rp17/2_restr1_Michal1.pdb_clean.pdb', 'test_data/rp17/2a_nonrestr2_Michal1.pdb_clean.pdb', 'test_data/rp17/3_nonrestr1_Michal1.pdb_clean.pdb', 'test_data/rp17/5_restr1_Michal3.pdb_clean.pdb']
- rna_tools.tools.rna_calc_rmsd.rna_calc_rmsd.sort_nicely(l)[source]¶
Sort the given list in the way that humans expect.
http://blog.codinghorror.com/sorting-for-humans-natural-sort-order/
rna_calc_rmsd_multi_targets.py¶
rna_calc_rmsd_multi_targets.py - calculate RMSDs of structures to multiple targets:
$ rna_calc_rmsd_multi_targets.py --models multi-targets/rp21/*.pdb --targets multi-targets/rp21/solutions/*.pdb --target-selection A:1-27+29-41 --model-selection A:1-27+29-41
CSV table produced:
21_solution_0_ChainA.pdb 21_solution_0_ChainB.pdb 21_solution_1_ChainA.pdb 21_solution_1_ChainB.pdb 21_solution_2.pdb mean min max sd
fn
21_3dRNA_1_rpr.pdb 12.17 12.11 12.17 12.11 12.11 12.13 12.11 12.17 0.03
21_Adamiak_1_rpr.pdb 4.64 4.61 4.64 4.61 4.64 4.63 4.61 4.64 0.01
21_ChenHighLig_1_rpr.pdb 4.01 3.97 4.01 3.97 4.07 4.01 3.97 4.07 0.04
21_Das_1_rpr.pdb 5.71 5.60 5.71 5.60 5.61 5.65 5.60 5.71 0.05
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Save rna_calc_rmsd_multi_targets_output.csv
usage: rna_calc_rmsd_multi_targets.py [-h] [-v] [--models MODELS [MODELS ...]]
[--targets TARGETS [TARGETS ...]]
[--output-csv OUTPUT_CSV]
[--model-selection MODEL_SELECTION]
[--target-selection TARGET_SELECTION]
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- -v, --verbose¶
be verbose
- --models <models>¶
- --targets <targets>¶
- --output-csv <output_csv>¶
- --model-selection <model_selection>¶
selection, e.g. A:10-16+20, where #16 residue is included
- --target-selection <target_selection>¶
selection, e.g. A:10-16+20, where #16 residue is included
rna_calc_rmsd_trafl¶
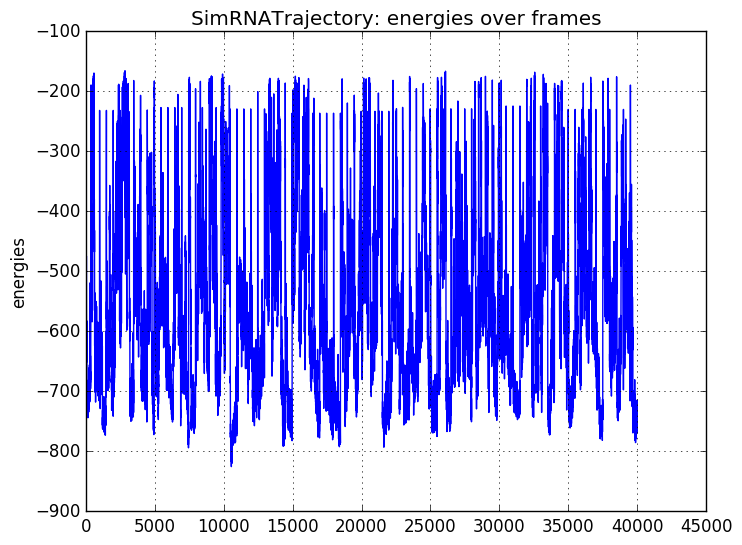
rna_calc_evo_rmsd¶
rmsd_calc_trafl - calculate RMSD of transition A->B based on a SimRNA trajectory
After this script, run:
rna_cal_rmsd_trafl_plot.py rmsd.txt
to get a plot like this:
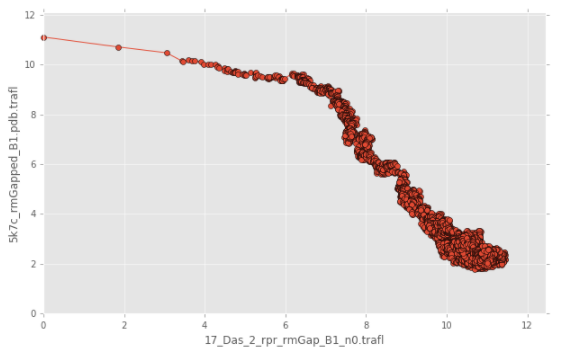
Prepare structures:
$ SimRNA -p 17_Das_2_rpr.pdb -n 0 -o 17_Das_2_rpr_n0 # no trafl, trafl will be added
$ SimRNA -p 5k7c_clean_onechain_renumber_as_puzzle_rpr_rmGapped.pdb -n 0 -o 5k7c_clean_onechain_renumber_as_puzzle_rpr_rmGapped
#(struc must be (~CG~) nope. It has to be a trajectory!)
and run:
$ rmsd_calc_trafl.py 17_Das_2_rpr.pdb.trafl 17_Das_2_rpr_n0.trafl 5k7c_clean_onechain_renumber_as_puzzle_rpr_rmGapped_n0.trafl rp17_rmsd.txt
> calc_rmsd_to_1st_frame
/Users/magnus/work/opt/simrna/SimRNA_64bitIntel_MacOSX_staticLibs/calc_rmsd_to_1st_frame 17_Das_2_rpr.pdb.trafl 17_Das_2_rpr.pdb_rmsd_e
< rmsd_out: 17_Das_2_rpr.pdb_rmsd_e
> struc: 17_Das_2_rpr_n0.trafl 2
> trafl: 17_Das_2_rpr.pdb.trafl 48
% saved: 17_Das_2_rpr.pdb.trafl_17_Das_2_rpr_n0.trafl
> calc_rmsd_to_1st_frame
/Users/magnus/work/opt/simrna/SimRNA_64bitIntel_MacOSX_staticLibs/calc_rmsd_to_1st_frame 17_Das_2_rpr.pdb.trafl_17_Das_2_rpr_n0.trafl 17_Das_2_rpr.pdb_rmsd_e_17_Das_2_rpr_n0_rmsd_e
< rmsd_out: 17_Das_2_rpr.pdb_rmsd_e_17_Das_2_rpr_n0_rmsd_e
> struc: 5k7c_clean_onechain_renumber_as_puzzle_rpr_rmGapped_n0.trafl 2
> trafl: 17_Das_2_rpr.pdb.trafl 48
% saved: 17_Das_2_rpr.pdb.trafl_5k7c_clean_onechain_renumber_as_puzzle_rpr_rmGapped_n0.trafl
> calc_rmsd_to_1st_frame
/Users/magnus/work/opt/simrna/SimRNA_64bitIntel_MacOSX_staticLibs/calc_rmsd_to_1st_frame 17_Das_2_rpr.pdb.trafl_5k7c_clean_onechain_renumber_as_puzzle_rpr_rmGapped_n0.trafl 17_Das_2_rpr.pdb_rmsd_e_5k7c_clean_onechain_renumber_as_puzzle_rpr_rmGapped_n0_rmsd_e
< rmsd_out: 17_Das_2_rpr.pdb_rmsd_e_5k7c_clean_onechain_renumber_as_puzzle_rpr_rmGapped_n0_rmsd_e
0.000 -695.634
0.000 -551.093
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
< out: rp17_rmsd.txt
Warning
calc_rmsd_to_1st_frame (SimRNA) is required and the path to the binary file is defined in config_local.
usage: rna_calc_evo_rmsd [-h] trafl struc1 struc2 rmsds_fn
- trafl¶
trafil
- struc1¶
structure A
- struc2¶
structure B
- rmsds_fn¶
output file
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
rna_cal_rmsd_trafl_plot¶
rna_cal_rmsd_trafl_plot - generate a plot based of <rmsd.txt> of rna_calc_evo_rmsd.py.
usage: rna_cal_rmsd_trafl_plot [-h] file
- file¶
rmsd.txt
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
rna_calc_rmsd_all_vs_all¶
rna_calc_rmsd_all_vs_all¶
rna_calc_rmsd_all_vs_all.py - calculate RMSDs all vs all and save it to a matrix
Examples:
rna_calc_rmsd_all_vs_all.py -i test_data -o test_output/rmsd_calc_dir.tsv
# of models: 4
... 1 test_data/struc1.pdb
... 2 test_data/struc2.pdb
... 3 test_data/struc3.pdb
... 4 test_data/struc4.pdb
The program is using (https://github.com/charnley/rmsd).
You can also use PyMOL to do align or fit:
python rna_calc_rmsd_all_vs_all.py -i test_data -o test_output/rmsd_calc_dir_align.mat -m align
# of models: 5
# test_data/2nd_triplex_FB_1AUA3_rpr.pdb test_data/struc1.pdb test_data/struc2.pdb test_data/struc3.pdb test_data/struc4.pdb
0.0 4.13 4.922 4.358 4.368
4.13 0.0 11.092 4.707 3.46
4.922 11.092 0.0 11.609 11.785
4.358 4.707 11.609 0.0 2.759
4.368 3.46 11.785 2.759 0.0
matrix was created! test
usage: rna_calc_rmsd_all_vs_all [-h] [-i INPUT_DIR] [-o MATRIX_FN] [-m METHOD]
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- -i <input_dir>, --input-dir <input_dir>¶
input folder with structures
- -o <matrix_fn>, --matrix-fn <matrix_fn>¶
ouput, matrix
- -m <method>, --method <method>¶
all-atom, pymol: align, fit
rna_calc_rmsd_all_vs_all.py - calculate RMSDs all vs all and save it to a matrix
Examples:
rna_calc_rmsd_all_vs_all.py -i test_data -o test_output/rmsd_calc_dir.tsv
# of models: 4
... 1 test_data/struc1.pdb
... 2 test_data/struc2.pdb
... 3 test_data/struc3.pdb
... 4 test_data/struc4.pdb
The program is using (https://github.com/charnley/rmsd).
You can also use PyMOL to do align or fit:
python rna_calc_rmsd_all_vs_all.py -i test_data -o test_output/rmsd_calc_dir_align.mat -m align
# of models: 5
# test_data/2nd_triplex_FB_1AUA3_rpr.pdb test_data/struc1.pdb test_data/struc2.pdb test_data/struc3.pdb test_data/struc4.pdb
0.0 4.13 4.922 4.358 4.368
4.13 0.0 11.092 4.707 3.46
4.922 11.092 0.0 11.609 11.785
4.358 4.707 11.609 0.0 2.759
4.368 3.46 11.785 2.759 0.0
matrix was created! test
- rna_tools.tools.rna_calc_rmsd.rna_calc_rmsd_all_vs_all.sort_nicely(l)[source]¶
Sort the given list in the way that humans expect. http://blog.codinghorror.com/sorting-for-humans-natural-sort-order/
Interaction Network Fidelity (INF)¶
rna_calc_inf.py¶
usage: rna_calc_inf.py [-h] [-t TARGET_FN] [-m NT]
[--ignore-files IGNORE_FILES] [-s SS] [--no-stacking]
[--debug] [--web] [-pr] [-sr] [--method METHOD]
[--target-selection TARGET_SELECTION]
[--model-selection MODEL_SELECTION]
[--renumber-residues] [--dont-remove-sel-files] [-f]
[-v] [-o OUT_FN]
files [files ...]
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- -t <target_fn>, --target_fn <target_fn>¶
pdb file
- -m <nt>, --number-of-threads <nt>¶
number of threads used for multiprocessing, if 1 then mp is not used (useful for debugging)!
- --ignore-files <ignore_files>¶
files to be ingored, .e.g, ‘solution’
- -s <ss>, --ss <ss>¶
A:(([[))]], works only for single chain (the chain is A by default)
- --no-stacking¶
default: use stacking, if this option on, don’t take into account stacking, WARNING/BUG: inf_all will be incorrectly calculated if stacking is off
- --debug¶
- --web¶
- -pr, --print-results¶
- -sr, --sort-results¶
- --method <method>¶
you can use mcannotate* or clarna (right now only clarna is tested)
- --target-selection <target_selection>¶
selection, e.g. A:10-16+20, where #16 residue is included
- --model-selection <model_selection>¶
selection, e.g. A:10-16+20, where #16 residue is included
- --renumber-residues¶
renumber residues from 1 to X for comparison with selection
- --dont-remove-sel-files¶
don’t remove temp files created based on target|model-selectionforce
- -f, --force¶
force to run ClaRNA even if <pdb>.outCR file is there, for will be auto True when selection defined
- -v, --verbose¶
be verbose, tell me more what’re doing
- -o <out_fn>, --out_fn <out_fn>¶
out csv file, be default inf.csv
A tool to calc inf_all, inf_stack, inf_WC, inf_nWC, SNS_WC, PPV_WC, SNS_nWC, PPV_nWC between two structures.
Mind, that ClaRNA is pretty slow, it takes even a few seconds to analyze a structure, so for, say, 1000 models you need a few hours.
How to make it faster?
First, you can use --number-of-threads to specify the number of cores used for multiprocessing.
Second, the procedure implemented in here is composed of two steps, first for each structure ClaRNA is used to generate an output with contacts, then these files are used for comparisons. So, if you want to re-run your analysis, you don’t have to re-run ClaRNA itself. Thus, be default ClaRNA is not executed if <model>.outCR is found next to the analyzed files. To change this behavior, force (--force) rna_calc_inf.py to re-run ClaRNA.
RNA filter (DCA)¶
Calculate distances based on given restrants on PDB files or SimRNA trajectories¶
rna_filter.py¶
rna_filter.py - calculate distances based on given restrants on PDB files or SimRNA trajectories.
Changes: weight is always 1 (at least for now). ,>,=,>=,<= .
[PREVIOUS DOCUMENTATION - TO BE REMOVED]
rna_filter.py -s 4gxy_rpr.pdb -r rp06_MohPairs.rfrestrs d:A5-A42 100.0 measured: 26.7465763417 [x] d:A11-A26 100.0 measured: 19.2863696104 [x]
- [mm] rp06$ git:(master) $ rna_filter.py -s 4gxy_rpr.pdb -r rp06_MohPairs.rfrestrs
d:A5-A42 100.0 measured: 26.7465763417 [x] d:A11-A26 100.0 measured: 19.2863696104 [x]
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File “/home/magnus/work-src/rna-pdb-tools/bin/rna_filter.py”, line 270, in <module>
calc_scores_for_pdbs(args.structures, restraints, args.verbose)
- File “/home/magnus/work-src/rna-pdb-tools/bin/rna_filter.py”, line 221, in calc_scores_for_pdbs
dist = get_distance(residues[h[0]][‘mb’], residues[h[1]][‘mb’])
KeyError: ‘A24’
correct, there is no A24 in this structure:
The format of restraints:
(d:A1-A2 < 10.0 1) = if distance between A1 and A2 lower than 10.0, score it with 1
Usage:
$ python rna_filter.py -r test_data/restraints.txt -s test_data/CG.pdb
d:A1-A2 10.0 measured: 6.58677550096 [x]
test_data/CG.pdb 1.0 1 out of 1
# $ python rna_filter.py -r test_data/restraints.txt -t test_data/CG.trafl
(d:A1-A2 < 10.0 1)|(d:A2-A1 <= 10 1)
restraints [('A1', 'A2', '<', '10.0', '1'), ('A2', 'A1', '<=', '10', '1')]
Frame #1 e:1252.26
mb for A1 [ 54.729 28.9375 41.421 ]
mb for A2 [ 55.3425 35.3605 42.7455]
d:A1-A2 6.58677550096
mb for A2 [ 55.3425 35.3605 42.7455]
mb for A1 [ 54.729 28.9375 41.421 ]
d:A2-A1 6.58677550096
# this ^ is off right now
usage: rna_filter.py [-h] -r RESTRAINTS_FN [-v]
[-s STRUCTURES [STRUCTURES ...]] [--offset OFFSET]
[-t TRAJECTORY]
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- -r <restraints_fn>, --restraints_fn <restraints_fn>¶
restraints_fn: Format: (d:A9-A41 < 10.0 1)|(d:A41-A9 <= 10 1)
- -v, --verbose¶
be verbose
- -s <structures>¶
structures
- --offset <offset>¶
use offset to adjust your restraints to numbering in PDB files, ade (1y26)pdb starts with 13, so offset is -12)
- -t <trajectory>¶
SimRNA trajectory
rna_dca_mapping.py¶
usage: rna_dca_mapping.py [-h] --seq SEQ --gseq GSEQ --dca DCA
[--offset OFFSET] [--noss] [--mss] [--verbose]
[--noshort]
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- --seq <seq>¶
seq fn in Fasta format
- --gseq <gseq>¶
gapped sequence and secondary structure (like in the alignment used for DCA) in Fasta format
- --dca <dca>¶
file with parsed interactions
- --offset <offset>¶
offset
- --noss¶
filter out ss from plot
- --mss¶
ss every each line
- --verbose¶
be verbose
- --noshort¶
filter out short interactions, dist in seq < 6 nt
Show distances in PyMOL¶
show_dists - show distances in PyMOL
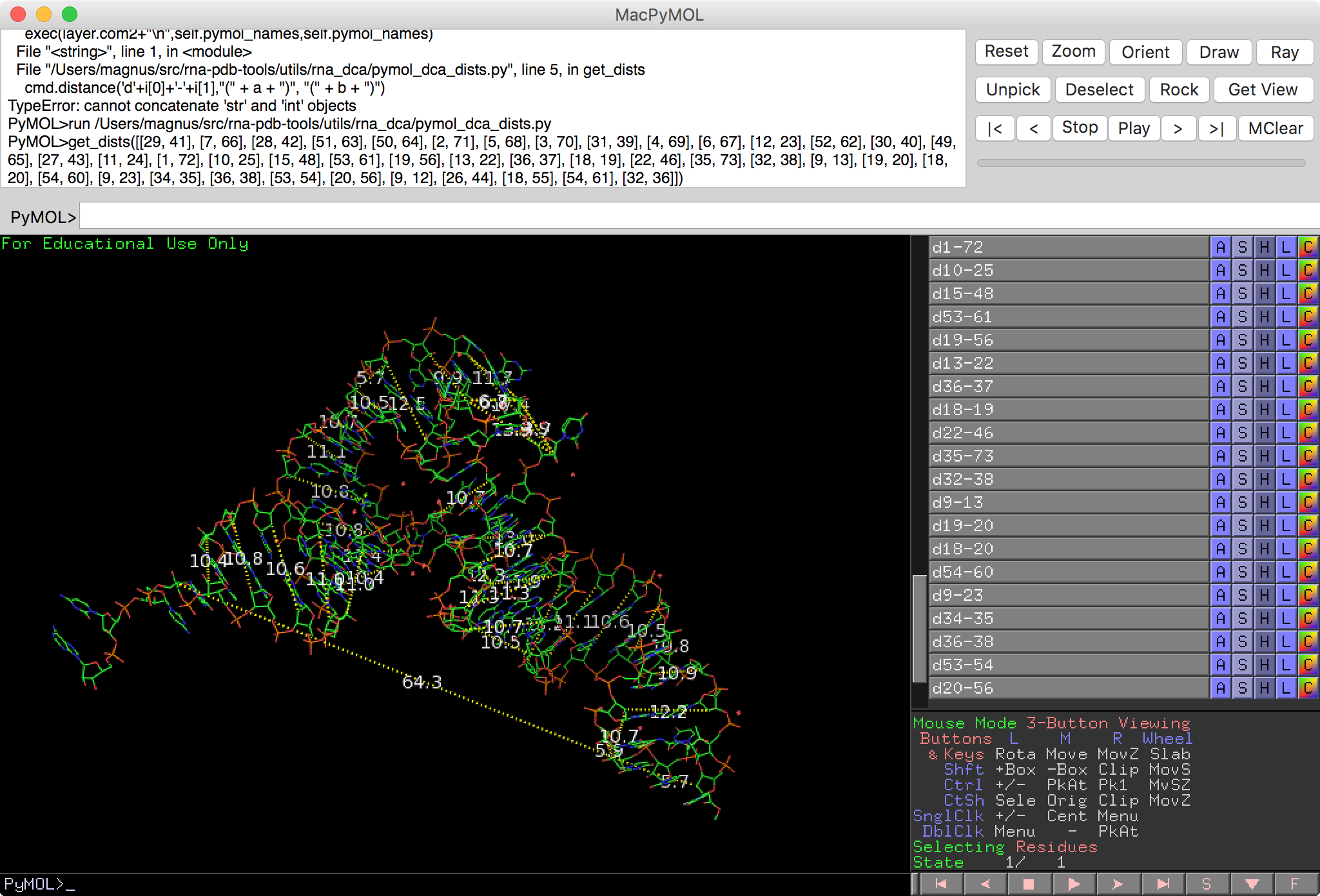
Usage:
PyMOL>show_dists([[1,2]])
1, 2, 3.41
Analyze an evolutionary coupling file. ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~`
rna_ec2x.py¶
rna_ex2x.py - analyze an evolutionary coupling file.
Files can be downloaded from https://marks.hms.harvard.edu/ev_rna/, e.g. RF00167.EC.interaction.csv
--pairs:
$ rna_ex2x.py RF00167.EC.interaction_LbyN.csv --pairs
[18, 78],[31, 39],[21, 75],[30, 40],[28, 42],[27, 43],[59, 67],[54, 72],[57, 69],[25, 45],[29, 41],[17, 79],[26, 44],[16, 80],[14, 82],[19, 77],[55, 71],[
15, 81],[34, 63],[56, 70],[58, 68],[35, 63],[26, 45],[35, 64],[32, 39],[54, 73],[24, 74],[16, 82],[24, 45],[24, 43],[32, 36],[25, 48],[48, 82],[36, 48],
usage: rna_ec2x.py [-h] [--sep SEP] [--chain CHAIN] [--ec-pairs]
[--ss-pairs SS_PAIRS] [--pairs-delta]
interaction_fn
- interaction_fn¶
interaction file
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- --sep <sep>¶
separator
- --chain <chain>¶
chain
- --ec-pairs¶
- --ss-pairs <ss_pairs>¶
file with secondary structure base pairs
- --pairs-delta¶
delta: ec-bp - ss-paris
Convert pairs to SimRNA restraints¶
rna_pairs2SimRNArestrs.py¶
rna_pairs2SimRNArestrs.py - convert pairs to SimRNA restraints
Example:
$ rna_pairs2SimRNArestrs.py rp06_pairs_delta.txt -v
# of pairs: 42
SLOPE A/2/MB A/172/MB 0 6 1
SLOPE A/2/MB A/172/MB 0 7 -1
SLOPE A/3/MB A/169/MB 0 6 1
SLOPE A/3/MB A/169/MB 0 7 -1
SLOPE A/12/MB A/32/MB 0 6 1
usage: rna_pairs2SimRNArestrs.py [-h] [--offset OFFSET] [--weight WEIGHT]
[--dist DIST] [--well] [-v]
pairs
- pairs¶
a file with [[2, 172], [3, 169], [12, 32], [13, 31]]
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- --offset <offset>¶
can be -10
- --weight <weight>¶
weight
- --dist <dist>¶
distances, for MOHCA use 25
- --well¶
well instead of slope
- -v, --verbose¶
be verbose
Get a list of base pairs for a given “fasta ss” file.¶
rna_ss_get_bps.py¶
rna_ss_get_bps.py - get a list of base pairs for a given “fasta ss” file.
Input file:
cat ade_ss.fa
>1y26
CGCUUCAUAUAAUCCUAAUGAUAUGGUUUGGGAGUUUCUACCAAGAGCCUUAAACUCUUGAUUAUGAAGUG
(((((((((...((((((.........))))))........((((((.......))))))..)))))))))%
Usage:
$ rna_ss_get_bps.py ade_ss.fa --offset 12
[[13, 83], [14, 82], [15, 81], [16, 80], [17, 79], [18, 78], [19, 77], [20, 76], [21, 75], [25, 45], [26, 44], [27, 43], [28, 42], [29, 41], [30, 40], [54, 72], [55, 71], [56, 70], [57, 69], [58, 68], [59, 67]]
Now it also work with pseudoknots.
usage: rna_ss_get_bps.py [-h] [--offset OFFSET] [-v] file
- file¶
file in the Fasta format
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- --offset <offset>¶
offset
- -v, --verbose¶
be verbose
Get a diff of pairs¶
rna_pairs_diff.py¶
rna_pairs_diff.py - get a diff of pairs
Usage:
$ rna_pairs_diff.py pistol_dca_all.bp pistol.bp
# of ec_paris: 31
# of ssbps : 18
dalta# : 13
[[4, 32], [6, 9], [6, 36], [6, 39], [9, 39], [13, 32], [16, 17], [17, 18], [22, 49], [29, 58]]
usage: rna_pairs_diff.py [-h] [-v] pairs1 pairs2
- pairs1¶
a list of pairs, A
- pairs2¶
a list of pairs to subtract, A-B, results in C(all pairs that are in A and are not in B
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- -v, --verbose¶
be verbose
Contacts classification & secondary structure detection¶
See also PyMOL4RNA for ways to visualize edges https://rna-tools.readthedocs.io/en/latest/pymol4rna.html
3DNA (contacts classification & secondary structure detection)¶
Python parser to 3dna <http://x3dna.org/>.
Installation:
# install the code from http://forum.x3dna.org/downloads/3dna-download/
Create a copy of the rna_x3dna_config_local_sample.py (remove "_sample") present in rna-tools/rna_tools/tools/rna_x3dna folder.
Edit this line :
BINARY_PATH = <path to your x3dna-dssr file>
matching the path with the path of your x3dna-dssr file.
e.g. in my case: BINARY_PATH = ~/bin/x3dna-dssr.bin
For one structure you can run this script as:
[mm] py3dna$ git:(master) ✗ ./rna_x3dna.py test_data/1xjr.pdb
test_data/1xjr.pdb
>1xjr nts=47 [1xjr] -- secondary structure derived by DSSR
gGAGUUCACCGAGGCCACGCGGAGUACGAUCGAGGGUACAGUGAAUU
..(((((((...((((.((((.....))..))..))).).)))))))
For multiple structures in the folder, run the script like this:
[mm] py3dna$ git:(master) ✗ ./rna_x3dna.py test_data/*
test_data/1xjr.pdb
>1xjr nts=47 [1xjr] -- secondary structure derived by DSSR
gGAGUUCACCGAGGCCACGCGGAGUACGAUCGAGGGUACAGUGAAUU
..(((((((...((((.((((.....))..))..))).).)))))))
test_data/6TNA.pdb
>6TNA nts=76 [6TNA] -- secondary structure derived by DSSR
GCGGAUUUAgCUCAGuuGGGAGAGCgCCAGAcUgAAgAPcUGGAGgUCcUGUGtPCGaUCCACAGAAUUCGCACCA
(((((((..((((.....[..)))).((((.........)))).....(((((..]....))))))))))))....
test_data/rp2_bujnicki_1_rpr.pdb
>rp2_bujnicki_1_rpr nts=100 [rp2_bujnicki_1_rpr] -- secondary structure derived by DSSR
CCGGAGGAACUACUG&CCGGCAGCCU&CCGGAGGAACUACUG&CCGGCAGCCU&CCGGAGGAACUACUG&CCGGCAGCCU&CCGGAGGAACUACUG&CCGGCAGCCU
[[[[(((.....(((&{{{{))))))&(((((((.....(.(&]]]]).))))&[[[[[[......[[[&))))]]].]]&}}}}(((.....(((&]]]]))))))
Warning
This script should not be used in this given form with Parallel because it process output files from x3dna that are named always in the same way, e.g. dssr-torsions.txt. #TODO
- class rna_tools.tools.rna_x3dna.rna_x3dna.x3DNA(pdbfn, show_log=False)[source]¶
Atributes:
curr_fn report
- get_ion_water_report()[source]¶
@todo File name: /tmp/tmp0pdNHS
no. of DNA/RNA chains: 0 [] no. of nucleotides: 174 no. of waters: 793 no. of metals: 33 [Na=29, Mg=1, K=3]
- get_torsions(outfn) str[source]¶
Get torsion angles into ‘torsion.csv’ file:
nt,id,res,alpha,beta,gamma,delta,epsilon,zeta,e-z,chi,phase-angle,sugar-type,ssZp,Dp,splay,bpseq 1,g,A.GTP1,nan,nan,142.1,89.5,-131.0,-78.3,-53(BI),-178.2(anti),358.6(C2’-exo),~C3’-endo,4.68,4.68,29.98,0 2,G,A.G2,-75.8,-167.0,57.2,79.5,-143.4,-69.7,-74(BI),-169.2(anti),5.8(C3’-endo),~C3’-endo,4.68,4.76,25.61,0
ClaRNA (contacts classification)¶
If you want to calculate “Interaction Network Fidelity (INF) and not only” see also rna_calc_inf
To run ClaRNA, see the documentaton below:
Usage:
$ rna_clarna_app.py ../../input/5k7c_clean_onechain_renumber_as_puzzle_srr.pdb ../../input/5k7c_clean_onechain_renumber_as_puzzle_srr.pdb
((((([[[[[[)))))........(.((....(]]]]]].)..(((......)))...)).)
Example
from rna_tools.utils.clarna_app import clarna_app
if __name__ == '__main__':
ss = '((((.[[[[[[.))))........((((.....]]]]]]...(((((....)))))..))))'
fnCRref = clarna_app.get_ClaRNA_output_from_dot_bracket(ss)
f = '../rna_calc_rmsd/test_data/pistol/5k7c_clean_onechain_renumber_as_puzzle_srr.pdb'
fnCR = clarna_app.clarna_run(f, force=False)
results = clarna_app.clarna_compare(fnCRref, fnCR)
print results #
#tmp_Z42i_..pdb.outCR 5k7c_clean_onechain_renumber_as_puzzle_srr.pdb.outCR 0.706 NA 0.865 NA 0.842 0.889 NA 0.000
- rna_tools.tools.clarna_app.rna_clarna_app.clarna_compare(target_cl_fn, i_cl_fn, verbose=False)[source]¶
Run ClaRNA compare (from rna_tools/tools/clarna_play).
- Returns:
a list target, fn, scores
Scores:
inf_all 0.706 inf_stack -999.999 -> NA inf_WC 0.865 inf_nWC -999.999 -> NA SNS_WC 0.842 PPV_WC 0.889 SNS_nWC NA PPV_nWC 0.000
Example of the list:
5k7c_clean_onechain_renumber_as_puzzle_srr.pdb pistol_thrs0.50A_clust01-000001_AA.pdb 0.642 NA 0.874 0.000 0.944 0.810 0.000 0.000s
use
results.split()[4]to get inf_WC
- rna_tools.tools.clarna_app.rna_clarna_app.clarna_run(fn, force=True, stacking=True, verbose=False)[source]¶
Run ClaRNA run
- rna_tools.tools.clarna_app.rna_clarna_app.get_ClaRNA_output_from_dot_bracket(ss, temp=True, verbose=False)[source]¶
Get dummy ClaRNA output out of dat bracket secondary structure (ss)
- Parameters:
ss (string) – secondary structure
- Returns:
a filename to ClaRNA output
- rna_tools.tools.clarna_app.rna_clarna_app.get_dot_bracket_from_ClaRNAoutput(inCR, verbose=False)[source]¶
In inCR file
Warning
This function requres ‘ClaRNAwd_to_vienaSS’ contact marcin.magnus@icloud.com
RNA 3D model quality assessment¶
Wrappers behind the server, http://genesilico.pl/mqapRNA (in short, mq)
RASP¶
This module contains functions for computing RASP potential
- class rna_tools.tools.mq.RASP.RASP.RASP(job_id=None)[source]¶
Wrapper class for running RASP automatically.
- executable = ['rasp_fd', 'rasp_profile_fd']¶
- program_name = ['rasp_fd', 'rasp_profile_fd']¶
- run(path_to_pdb, global_energy_score=True, potentials=['c3', 'bb', 'bbr', 'all'], handler=True, verbose=False)[source]¶
Compute RASP potential for a single file
rasp_fdgenerates:output_all.txt:-9869.61 66447 -0.148534 0 0 0
rasp_profile_fdgenerates:profile_all.txt:C 1 R -775.038 C 2 R -1164.22 U 3 R -2054.17 G 4 R -1601.13 [..]
- Input:
path_to_pdb = path to PDB file
potential_type = all, bbr or c3
global_energy_score = True/False (See Output), default=True
hander = True (if you use PYRO)/FALSE otherwise
- Output:
the output depends on global_enery_score value T/F You might get:
-9869.61profile [('C', 1, 'R', -775.03800000000001), ('C', 2, 'R', -1164.22) ..
Dfire¶
This module contains functions for computing Dfire potential
Installation:
git clone https://github.com/tcgriffith/dfire_rna.git make # add DFIRE_RNA_HOME to .bashrc
RNAkb¶
This module contains functions for computing RNAkb potential
It seems that this is impossible to run RNAkb in full atom mode. So this works only in 5 pt (5 points/atom per residue) mode.
- class rna_tools.tools.mq.RNAkb.RNAkb.RNAkb(job_id='', sandbox=False)[source]¶
Wrapper class for running RNAkb automatically.
- executable = ['/usr/local/gromacs/bin/pdb2gmx', '/usr/local/gromacs/bin/make_ndx', '/usr/local/gromacs/bin/editconf', '/usr/local/gromacs/bin/grompp', '/usr/local/gromacs/bin/mdrun']¶
- run(name, potential_type, verbose=False)[source]¶
Compute RNAkb potential for a single file
- Parameters:
- Returns:
a list of energies (strings) [‘2.57116e+05’, ‘1.62131e+03’, ‘7.82459e+02’, ‘3.00789e-01’, ‘0.00000e+00’, ‘0.00000e+00’, ‘-2.51238e-03’, ‘0.00000e+00’, ‘2.59520e+05’, ‘2.54174e-09’, ‘2.59520e+05’]
Warning
‘aa’ does not work because of “a line longer than 4095 characters”
The function parses:
Statistics over 1 steps using 1 frames Energies (kJ/mol) Bond Angle Proper Dih. Improper Dih. LJ-14 2.44111e+05 1.76069e+03 8.12947e+02 1.82656e-01 0.00000e+00 Coulomb-14 LJ (SR) Coulomb (SR) Potential Kinetic En. 0.00000e+00 -1.94624e-03 0.00000e+00 2.46685e+05 2.43227e-09 Total Energy Temperature Pressure (bar) 2.46685e+05 6.67884e-10 -5.94232e+04 Total Virial # ['Statistics', 'over', '1', 'steps', 'using', '1', 'frames', 'Energies', '(kJ/mol)', 'Bond', 'Angle', 'Proper', 'Dih.', 'Improper', 'Dih.', 'LJ-14', '2.44111e+05', '1.76069e+03', '8.12947e+02', '1.82656e-01', '0.00000e+00', 'Coulomb-14', 'LJ', '(SR)', 'Coulomb', '(SR)', 'Potential', 'Kinetic', 'En.', '0.00000e+00', '-1.94624e-03', '0.00000e+00', '2.46685e+05', '2.43227e-09', 'Total', 'Energy', 'Temperature', 'Pressure', '(bar)', '2.46685e+05', '6.67884e-10', '-5.94232e+04', 'Total', 'Virial'] result[6] is really the RNAkb
rna_mq_rnakb.py¶
Standalone tool to run the RNAkb class in the terminal.
All atom mode does not really work, see the documentation of the RNAkb class.
usage: rna_mq_rnakb.py [-h] [-v] [-p POTENTIAL] file [file ...]
- file¶
a PDB file, one or more
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- -v, --verbose¶
be verbose
- -p <potential>, --potential <potential>¶
5pt
QRNA¶
eSCORE¶
This module contains functions for computing eSCORE
Install:
pip install barnaba # tested with barnaba==0.1.7
Output:
$ baRNAba ESCORE --pdb ../test/1a9n.pdb --ff /Users/magnus/work/opt/barnaba/barnaba_201128/test/data/1S72.pdb
# your output will be written to files with prefix outfile.ESCORE
# KDE computed. Bandwidth= 0.25 using 10655 base-pairs# Loaded sample ../test/1a9n.pdb
# Frame ESCORE
0 4.1693e-01
The eSCORE could be also accessed via Python:
from barnaba import escore
Escore = escore.Escore([path_to_pdb])
(..)
# see example_12_escore.ipynb of barnaba package https://github.com/srnas/barnaba
It does not work on M1 mac (problem to compile mdtraj).
3dRNAscore¶
This module contains functions for computing 3dRNAscore
Install:
make # make clean if you don't have clean
At Mac there is a problem (201128, 211103):
(py37) [mx] example$ ../bin/3dRNAscore -s:l score.in >score.txt
[1] 69818 segmentation fault ../bin/3dRNAscore -s:l score.in > score.txt
RNA3DCNN¶
This module contains functions for computing RNA3DCNN potential
Output:
Trainable params: 4,282,801
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
Scores for each nucleotide in /var/folders/yc/ssr9692s5fzf7k165grnhpk80000gp/T/tmptg6jy2ud/query.pdb:
[[ 0.02462262]
[ 0.03271335]
[ 0.06199259]
[ 0.02006263]
[ 0.05937254]
[ 0.12025979]
[ 0.20201728]
[ 0.24463326]
[ 0.43518737]
[ 0.7260638 ]
[ 0.6140108 ]
[ 0.6588027 ]
[ 0.7668936 ]
[ 0.4776191 ]
[ 0.39859247]
[ 0.572009 ]
[ 0.64892375]
[ 0.11587611]
[ 0.0560993 ]
[ 0.05285829]
[ 0.0167731 ]
[ 0.01759553]
[ 0.02143204]
[-0.01818037]]
Total score for /var/folders/yc/ssr9692s5fzf7k165grnhpk80000gp/T/tmptg6jy2ud/query.pdb is 6.3262305
If missing atoms:
Total params: 4,282,801
Trainable params: 4,282,801
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
There is no atom O5' in residue 620A in chain A in PDB /var/folders/yc/ssr9692s5fzf7k165grnhpk80000gp/T/tmpx87uus6x/query.pdb.
There is no atom O5' in residue 635A in chain B in PDB /var/folders/yc/ssr9692s5fzf7k165grnhpk80000gp/T/tmpx87uus6x/query.pdb.
There is no atom O5' in residue 1750G in chain C in PDB /var/folders/yc/ssr9692s5fzf7k165grnhpk80000gp/T/tmpx87uus6x/query.pdb.
Scores for each nucleotide in /var/folders/yc/ssr9692s5fzf7k165grnhpk80000gp/T/tmpx87uus6x/query.pdb:
[]
Total score for /var/folders/yc/ssr9692s5fzf7k165grnhpk80000gp/T/tmpx87uus6x/query.pdb is 0.0
FARNA¶
Wrapper for ROSETTA software for structure prediction of small RNA sequences
- class rna_tools.tools.mq.FARNA.FARNA.FARNA(sequence='test', seq_name='test', job_id=None)[source]¶
Wrapper class for running ROSETTA scoring function automatically.
- best_energy = ''¶
- cleanup()[source]¶
Run this method when you are done with this wrapper. It deletes sandbox, some of it’s childrem may do some other cleanup here.
- db_path = ''¶
- executable = 'rna_minimize'¶
- get_result()[source]¶
Parse and get result from score file created during ROSETTA run
All results are kept in self.result, but only global score is returned
- input_file = ''¶
- input_fn = 'seq.fasta'¶
- program_name = 'farna'¶
- run(pdb_file, hires, verbose=False, system=False)[source]¶
Compute FARNA potential for a single file
- Parameters:
file (* pdb_file = path to pdb) –
True/False (* global_energy_score =) –
- Output:
A list of energies, e.g:
['-21.721', '-0.899', '-20.961', '-84.498', '-16.574', '-180.939', '11.549', '7.475', '-17.257', '-306.324', '0.0', '0.0', '17.503', '0.0']
??? or a dictionary of lists of local scores, eg:
{ 'N_BS': [17.0, -0.70039, -0.720981, -0.685238, -0.734146, ... ], 'atom_pair_constraint': [0.0, -0.764688, -0.773833, ...], ... }
- src_bin = ''¶
ClashScore¶
- class rna_tools.tools.mq.ClashScore.ClashScore.ClashScore[source]¶
ClashScore: Wrapper class for running phenix.clashscore
- run(fn, verbose=False)[source]¶
- Parameters:
fn (string) – path to a file
verbose (bool) – be verbose
- Returns:
clashscore (float)
Example:
/Applications/phenix-1.18.2-3874/build/bin/phenix.clashscore test/1xjrA.pdb Using electron cloud x-H distances and vdW radii Adding H/D atoms with reduce... Bad Clashes >= 0.4 Angstrom: A 17 A N1 A 34 G N1 :0.430 clashscore = 0.66 test/1xjrA.pdb 0.66 /Applications/phenix-1.18.2-3874/build/bin/phenix.clashscore test/1xjrA_M1.pdb Using electron cloud x-H distances and vdW radii Adding H/D atoms with reduce... Bad Clashes >= 0.4 Angstrom: A 41 G H2' A 42 U OP1 :0.738 A 25 U H6 A 25 U HO2' :0.659 A 46 U H2' A 47 U OP2 :0.656 A 29 A H5'' A 30 U O2' :0.623 (...) A 24 G O2' A 26 A C8 :0.410 A 42 U O2' A 43 G H8 :0.409 A 43 G H2' A 44 A O4' :0.408 A 28 G C8 A 28 G O2' :0.403 clashscore = 15.45 test/1xjrA_M1.pdb 15.45 # so the output is clashscore = 15.45
AnalyzeGeometry¶
This module contains functions for computing AnalyzeGeomotery.
- class rna_tools.tools.mq.AnalyzeGeometry.AnalyzeGeometry.AnalyzeGeometry(verbose=False)[source]¶
Wrapper class for running clashscore
Note
Sequence is required to get the length to calculate % of corrent residues.
- run(name, verbose=False)[source]¶
- Parameters:
name (str) – the path of the file to wrap
verbose (boolen) – be verbose
- Returns:
score; % of Backbone torsion suites (# of them per seq)
- Return type:
Output:
----------Backbone torsion suites---------- Suite ID suite suiteness triaged angle A A 3 !! 0.000 delta G A 4 !! 0.000 epsilon-1 G A 11 !! 0.000 None C A 20 !! 0.000 gamma U A 25 !! 0.000 delta A A 26 !! 0.000 delta-1 A A 29 !! 0.000 None U A 30 !! 0.000 epsilon-1 G A 41 !! 0.000 delta U A 42 !! 0.000 delta-1 A A 45 !! 0.000 delta U A 46 !! 0.000 epsilon-1 U A 47 !! 0.000 delta-1 11 suites triaged and 0 incomplete leaving 35 suites 13/46 suite outliers present Average suiteness: 0.490 13 # count lines after 'traged angle' and minus 3 (# of last lines) test/1xjrA_M1.pdb 34.7826Output for a perfect structure:
/Applications/phenix-1.18.2-3874/build/bin/phenix.rna_validate /Users/magnus/work/src/rna-tools/rna_tools/input/mq/5e3hBC.pdb CGACGCUAGCGUACGCUAGCGUCG AnalyzeGeomtery:: ----------Backbone bond lenths---------- All bonds within 4.0 sigma of ideal values. ----------Backbone bond angles---------- All angles within 4.0 sigma of ideal values. ----------Sugar pucker---------- All puckers have reasonable geometry. ----------Backbone torsion suites---------- 0 suites triaged and 0 incomplete leaving 24 suites All RNA torsion suites are reasonable. Average suiteness: 0.766
RNA 3D structure prediction¶
ROSETTA¶
A set of wrappers around Rosetta (https://www.rosettacommons.org/), mostly based on C. Y. Cheng, F. C. Chou, and R. Das, Modeling complex RNA tertiary folds with Rosetta, 1st ed., vol. 553. Elsevier Inc., 2015. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0076687914000524
Run (modeling)¶
rna_rosetta_run.py¶
rna_rosetta_run.py - prepare & run ROSETTA simulations
Based on C. Y. Cheng, F. C. Chou, and R. Das, Modeling complex RNA tertiary folds with Rosetta, 1st ed., vol. 553. Elsevier Inc., 2015. http: // www.sciencedirect.com / science / article / pii / S0076687914000524
The script makes(1) a folder for you job, with seq.fa, ss.fa, input file is copied as input.fa to the folder(2) make helices(3) prepare rosetta input files(4) sends jobs to the cluster.
The header is take from the fast file(`` > /header / ``) not from the filename of your Fasta file.
I discovered this:
qstat -xml | tr '\n' ' ' | sed 's#<job_list[^>]*>#\n#g' \
> | sed ‘s#<[^>]*>##g’ | grep “ “ | column -t
(https://stackoverflow.com/questions/26104116/qstat-and-long-job-names) so there is now need to shorted my job ids.
Helix¶
Run:
rna_rosetta_run.py -i -e -r -g -c 200 cp20.fa
-i:
# prepare a folder for a run
>cp20
AUUAUCAAGAAUCUCAAAGAGAGAUAGCAACCUGCAAUAACGAGCAAGGUGCUAAAAUAGAUAAGCCAAAUUCAAUUGGAAAAAAUGUUAA
.(((((....(((((.....)))))(((..(((((..[[[[..)).))).)))......))))).((((......)))).......]]]].
[peyote2] ~ rna_rosetta_run.py -i cp20.fa
run rosetta for:
cp20
AUUAUCAAGAAUCUCAAAGAGAGAUAGCAACCUGCAAUAACGAGCAAGGUGCUAAAAUAGAUAAGCCAAAUUCAAUUGGAAAAAAUGUUAA
.(((((....(((((.....)))))(((..(((((..[[[[..)).))).)))......))))).((((......)))).......]]]].
/home / magnus // cp20 / created
Seq & ss created
Troubleshooting.
If one of the helices is missing you will get:
IOError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'helix1.out'
rosetta_submit.py README_FARFAR o 500 100 taf
Could not find: README_FARFAR
and the problem was a1 and g8 pairing:
outputting command line to: helix0.RUN # previous helix #0
Sequence: AUGG CCGG
Secstruc: (((())))
Not complementary at positions a1 and g8!
Sequence: GUGGG CCCAU
Secstruc: ((((()))))
Writing to fasta file: helix2.fasta # next helix #2
My case with a modeling of rp12
Sequence: cc gc Secstruc: (()) Not complementary at positions 1 and 4!
edit the secondary structure, run the program with -i(init, to overwrite seq.fa, ss.fa) and then it works.
Notes:
rp17hc 6 characters
usage: rna_rosetta_run.py [-h] [-i] [-e] [-r] [-g] [-m MOTIF] [-n NSTRUC]
[-c CPUS] [--sandbox SANDBOX]
file
- file¶
file: > a04 UAUAACAUAUAAUUUUGACAAUAUGGGUCAUAAGUUUCUACCGGAAUACCGUAAAUAUUCUGACUAUGUAUA ((((.((((…((.((((…….)))).))……..(.(((((…….))))).)..))))))))
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- -i, --init¶
prepare _folder with seq and ss
- -e, --helices¶
produce h(E)lices
- -r, --rosetta¶
prepare rosetta files (still you need go to send jobs to a cluster)
- -g, --go¶
send jobs to a cluster(run qsubMINI)
- -m <motif>, --motif <motif>¶
include a motif file, e.g. -s E-loop_1q9a_mutated_no_flanks_renumber.pdb
- -n <nstruc>, --nstruc <nstruc>¶
# of structures you want to get
- -c <cpus>, --cpus <cpus>¶
# of cpus to be used
- --sandbox <sandbox>¶
where to run it (default: RNA_ROSETTA_RUN_ROOT_DIR_MODELING
rna_rosetta_run.py - prepare & run ROSETTA simulations
Based on C. Y. Cheng, F. C. Chou, and R. Das, Modeling complex RNA tertiary folds with Rosetta, 1st ed., vol. 553. Elsevier Inc., 2015. http: // www.sciencedirect.com / science / article / pii / S0076687914000524
The script makes(1) a folder for you job, with seq.fa, ss.fa, input file is copied as input.fa to the folder(2) make helices(3) prepare rosetta input files(4) sends jobs to the cluster.
The header is take from the fast file(`` > /header / ``) not from the filename of your Fasta file.
I discovered this:
qstat -xml | tr '\n' ' ' | sed 's#<job_list[^>]*>#\n#g' \
> | sed ‘s#<[^>]*>##g’ | grep “ “ | column -t
(https://stackoverflow.com/questions/26104116/qstat-and-long-job-names) so there is now need to shorted my job ids.
Helix¶
Run:
rna_rosetta_run.py -i -e -r -g -c 200 cp20.fa
-i:
# prepare a folder for a run
>cp20
AUUAUCAAGAAUCUCAAAGAGAGAUAGCAACCUGCAAUAACGAGCAAGGUGCUAAAAUAGAUAAGCCAAAUUCAAUUGGAAAAAAUGUUAA
.(((((....(((((.....)))))(((..(((((..[[[[..)).))).)))......))))).((((......)))).......]]]].
[peyote2] ~ rna_rosetta_run.py -i cp20.fa
run rosetta for:
cp20
AUUAUCAAGAAUCUCAAAGAGAGAUAGCAACCUGCAAUAACGAGCAAGGUGCUAAAAUAGAUAAGCCAAAUUCAAUUGGAAAAAAUGUUAA
.(((((....(((((.....)))))(((..(((((..[[[[..)).))).)))......))))).((((......)))).......]]]].
/home / magnus // cp20 / created
Seq & ss created
Troubleshooting.
If one of the helices is missing you will get:
IOError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'helix1.out'
rosetta_submit.py README_FARFAR o 500 100 taf
Could not find: README_FARFAR
and the problem was a1 and g8 pairing:
outputting command line to: helix0.RUN # previous helix #0
Sequence: AUGG CCGG
Secstruc: (((())))
Not complementary at positions a1 and g8!
Sequence: GUGGG CCCAU
Secstruc: ((((()))))
Writing to fasta file: helix2.fasta # next helix #2
My case with a modeling of rp12
Sequence: cc gc Secstruc: (()) Not complementary at positions 1 and 4!
edit the secondary structure, run the program with -i(init, to overwrite seq.fa, ss.fa) and then it works.
Notes:
rp17hc 6 characters
- class rna_tools.tools.rna_rosetta.rna_rosetta_run.CustomFormatter(prog, indent_increment=2, max_help_position=24, width=None)[source]¶
- rna_tools.tools.rna_rosetta.rna_rosetta_run.prepare_folder(args, header, seq, ss, path)[source]¶
Make folder for you job, with seq.fa, ss.fa, input file is copied as input.fa to the folder.
For ss lowercase is needed when used with motifs, otherwise:
[peyote2] aa20$ rna_rosetta_run.py -r -m E-loop_1q9a_mutated_no_flanks_renumber_for_acy20.pdb ~/aa20.fa 2019-05-03 21:31:30,842 rpt_config_local.py::<module>::rpt_config_local loading... run rosetta for: aa20 UACGUUCAUCAUCCGUUUGGAUGACGGAAGUAAGCGAAAGCUGAAGGAACGCAUG ..(((((.((((((....))))))..[.....(((....)))....)))))]... rna_denovo_setup.py -fasta seq.fa -secstruct_file ss.fa -cycles 20000 -no_minimize -nstruct 50 -s E-loop_1q9a_mutated_no_flanks_renumber_for_acy20.pdb -silent helix0.out helix1.out helix2.out -input_silent_res 3-7 47-51 9-14 19-24 33-35 40-42 Sequence: UACGUUCAUCAUCCGUUUGGAUGACGGAAGUAAGCGAAAGCUGAAGGAACGCAUG Secstruc: ..(((((.((((((....))))))..[.....(((....)))....)))))]... aaguagaag AAGUAGAAG Traceback (most recent call last): File "/home/magnus/opt/rosetta_src_2016.13.58602_bundle/tools/rna_tools/bin//rna_denovo_setup.py", line 170, in <module> raise ValueError('The sequence in %s does not match input sequence!!' % pdb) ValueError: The sequence in E-loop_1q9a_mutated_no_flanks_renumber_for_acy20.pdb does not match input sequence!! rosetta_submit.py README_FARFAR o 200 100 aa20_ Could not find: README_FARFAR
- rna_tools.tools.rna_rosetta.rna_rosetta_run.prepare_helices()[source]¶
Make helices(wrapper around ‘helix_preassemble_setup.py’)
Warning
I think multiprocessing of helixX.run does not work.
- rna_tools.tools.rna_rosetta.rna_rosetta_run.prepare_rosetta(header, cpus, motif, nstruc)[source]¶
Prepare ROSETTA using rna_denovo_setup.py
cpus is used to calc nstruc per job to get 10k structures per full run:
:param nstruc: how many structures you want to obtain :type nstruc: int :param nstruct = int: :type nstruct = int: math.floor(20000 / cpus) :param motif: motif file; e.g., -s E-loop_1q9a_mutated_no_flanks_renumber.pdb :param 50: :type 50: nstruc) = 10k / 200 (cpus
Get a number of structures¶
rna_rosetta_n.py¶
rna_roseta_n.py - show me # of structure in a silent file
Example:
$ rna_rosetta_n.py ade.out
21594
$ rna_rosetta_n.py *out
default.out 100
default1.out 200
default2.out 200
default3.out 100
usage: rna_rosetta_n.py [-h] [-v] [-0] file [file ...]
- file¶
ade.out
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- -v, --verbose¶
- -0, --zero¶
rna_roseta_n.py - show me # of structure in a silent file
Example:
$ rna_rosetta_n.py ade.out
21594
$ rna_rosetta_n.py *out
default.out 100
default1.out 200
default2.out 200
default3.out 100
Get a head of a Rosetta silent file¶
rna_rosetta_n.py¶
rna_roseta_head.py - get a head of a Rosetta silent file.
Example:
$ rna_rosetta_head.py -n 10000 thf.out
# a new file will be created, thf_10000.out
Silent file:
[peyote2] thf head -n 100 thf.out
SEQUENCE: ggagaguagaugauucgcguuaagugugugugaaugggaugucgucacacaacgaagcgagagcgcggugaaucauugcauccgcucca
SCORE: score rna_data_backbone rna_vdw rna_base_backbone rna_backbone_backbone rna_repulsive rna_base_pair rna_base_axis rna_base_stagger rna_base_stack rna_base_stack_axis rna_rg atom_pair_constraint linear_chainbreak N_WC N_NWC N_BS description
REMARK BINARY SILENTFILE
SCORE: -601.975 0.000 31.113 -16.960 -3.888 20.501 -302.742 -38.531 -158.004 -80.764 -110.053 23.750 0.000 33.601 32 6 86 S_000001_000
FOLD_TREE EDGE 1 4 -1 JEDGE 4 85 1 C4 C2 END EDGE 4 5 -1 EDGE 85 80 -1 EDGE 85 89 -1 JEDGE 80 40 5 C4 C2 END EDGE 80 78 -1 EDGE 40 43 -1 EDGE 40 33 -1 JEDGE 33 45 4 C4 C2 END EDGE 45 54 -1 EDGE 45 44 -1 EDGE 33 20 -1 JEDGE 20 65 3 C2 C4 END EDGE 65 67 -1 EDGE 20 17 -1 EDGE 65 63 -1 JEDGE 17 69 2 C4 C2 END JEDGE 63 58 6 C4 C2 END EDGE 17 6 -1 EDGE 58 59 -1 EDGE 63 60 -1 EDGE 69 77 -1 EDGE 58 55 -1 EDGE 69 68 -1 S_000001_000
RT -0.987743 0.139354 0.0703103 0.135963 0.989404 -0.0509304 -0.0766626 -0.0407466 -0.996224 6.25631 0.103544 0.0647696 S_000001_000
RT -0.98312 0.1587 -0.091045 0.166923 0.981743 -0.0912024 0.074909 -0.10486 -0.991662 5.89962 -1.95819 -0.1075 S_000001_000
RT -0.987645 0.154078 0.0285994 0.153854 0.988044 -0.00989514 -0.0297821 -0.00537275 -0.999542 6.13138 1.047 0.115722 S_000001_000
RT -0.989884 0.140722 0.0180554 0.140036 0.989532 -0.0348618 -0.0227723 -0.0319807 -0.999229 6.21787 0.201588 -0.0264223 S_000001_000
RT -0.988455 0.134013 0.0706914 0.134924 0.990822 0.00825457 -0.0689364 0.0176973 -0.997464 6.19447 0.189237 0.125791 S_000001_000
RT -0.990412 0.138036 0.00546261 0.137927 0.990299 -0.0168644 -0.00773751 -0.0159492 -0.999843 6.25456 0.0842849 -0.0135807 S_000001_000
ANNOTATED_SEQUENCE: g[RGU:LowerRNA:Virtual_Phosphate]gaga[RAD:rna_cutpoint_lower]g[RGU:rna_cutpoint_upper]uagaugauucgcguuaagugugugugaaugggauguc[RCY:rna_cutpoint_lower]g[RGU:rna_cutpoint_upper]ucacacaacg[RGU:rna_cutpoint_lower]a[RAD:rna_cutpoint_upper]agcg[RGU:rna_cutpoint_lower]a[RAD:rna_cutpoint_upper]gagcgcg[RGU:rna_cutpoint_lower]g[RGU:rna_cutpoint_upper]ugaaucauu[URA:rna_cutpoint_lower]g[RGU:rna_cutpoint_upper]cauccgcucca[RAD:UpperRNA] S_000001_000
Le3nY9smsa4zEMGdvAA+z+e
It seems to work:
-rw-rw-r-- 1 magnus users 474M 2017-08-06 05:25 thf_10000.out
-rw -rw-r-- 1 magnus users 947M 2017-08-06 04:54 thf.out
[peyote2] thf rna_rosetta_n.py thf_10000.out
10000
usage: rna_rosetta_n.py [-h] [-v] [-n NSTRUC] file
- file¶
ade.out
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- -v, --verbose¶
- -n <nstruc>, --nstruc <nstruc>¶
rna_roseta_head.py - get a head of a Rosetta silent file.
Example:
$ rna_rosetta_head.py -n 10000 thf.out
# a new file will be created, thf_10000.out
Silent file:
[peyote2] thf head -n 100 thf.out
SEQUENCE: ggagaguagaugauucgcguuaagugugugugaaugggaugucgucacacaacgaagcgagagcgcggugaaucauugcauccgcucca
SCORE: score rna_data_backbone rna_vdw rna_base_backbone rna_backbone_backbone rna_repulsive rna_base_pair rna_base_axis rna_base_stagger rna_base_stack rna_base_stack_axis rna_rg atom_pair_constraint linear_chainbreak N_WC N_NWC N_BS description
REMARK BINARY SILENTFILE
SCORE: -601.975 0.000 31.113 -16.960 -3.888 20.501 -302.742 -38.531 -158.004 -80.764 -110.053 23.750 0.000 33.601 32 6 86 S_000001_000
FOLD_TREE EDGE 1 4 -1 JEDGE 4 85 1 C4 C2 END EDGE 4 5 -1 EDGE 85 80 -1 EDGE 85 89 -1 JEDGE 80 40 5 C4 C2 END EDGE 80 78 -1 EDGE 40 43 -1 EDGE 40 33 -1 JEDGE 33 45 4 C4 C2 END EDGE 45 54 -1 EDGE 45 44 -1 EDGE 33 20 -1 JEDGE 20 65 3 C2 C4 END EDGE 65 67 -1 EDGE 20 17 -1 EDGE 65 63 -1 JEDGE 17 69 2 C4 C2 END JEDGE 63 58 6 C4 C2 END EDGE 17 6 -1 EDGE 58 59 -1 EDGE 63 60 -1 EDGE 69 77 -1 EDGE 58 55 -1 EDGE 69 68 -1 S_000001_000
RT -0.987743 0.139354 0.0703103 0.135963 0.989404 -0.0509304 -0.0766626 -0.0407466 -0.996224 6.25631 0.103544 0.0647696 S_000001_000
RT -0.98312 0.1587 -0.091045 0.166923 0.981743 -0.0912024 0.074909 -0.10486 -0.991662 5.89962 -1.95819 -0.1075 S_000001_000
RT -0.987645 0.154078 0.0285994 0.153854 0.988044 -0.00989514 -0.0297821 -0.00537275 -0.999542 6.13138 1.047 0.115722 S_000001_000
RT -0.989884 0.140722 0.0180554 0.140036 0.989532 -0.0348618 -0.0227723 -0.0319807 -0.999229 6.21787 0.201588 -0.0264223 S_000001_000
RT -0.988455 0.134013 0.0706914 0.134924 0.990822 0.00825457 -0.0689364 0.0176973 -0.997464 6.19447 0.189237 0.125791 S_000001_000
RT -0.990412 0.138036 0.00546261 0.137927 0.990299 -0.0168644 -0.00773751 -0.0159492 -0.999843 6.25456 0.0842849 -0.0135807 S_000001_000
ANNOTATED_SEQUENCE: g[RGU:LowerRNA:Virtual_Phosphate]gaga[RAD:rna_cutpoint_lower]g[RGU:rna_cutpoint_upper]uagaugauucgcguuaagugugugugaaugggauguc[RCY:rna_cutpoint_lower]g[RGU:rna_cutpoint_upper]ucacacaacg[RGU:rna_cutpoint_lower]a[RAD:rna_cutpoint_upper]agcg[RGU:rna_cutpoint_lower]a[RAD:rna_cutpoint_upper]gagcgcg[RGU:rna_cutpoint_lower]g[RGU:rna_cutpoint_upper]ugaaucauu[URA:rna_cutpoint_lower]g[RGU:rna_cutpoint_upper]cauccgcucca[RAD:UpperRNA] S_000001_000
Le3nY9smsa4zEMGdvAA+z+e
It seems to work:
-rw-rw-r-- 1 magnus users 474M 2017-08-06 05:25 thf_10000.out
-rw -rw-r-- 1 magnus users 947M 2017-08-06 04:54 thf.out
[peyote2] thf rna_rosetta_n.py thf_10000.out
10000
Cluster¶
rna_rosetta_cluster.py¶
rna_rosetta_cluster.py - cluster silent Rosetta files
A wrapper to ROSETTA tools for RNA modeling
Based on C. Y. Cheng, F. C. Chou, and R. Das, Modeling complex RNA tertiary folds with Rosetta, 1st ed., vol. 553. Elsevier Inc., 2015. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0076687914000524
rna_rosetta_cluster.py ade_min.out 20000
Take n * 0.005 (.5%) of all frames and put them into selected.out. Then the tool clusters this selected.out.
usage: rna_rosetta_cluster.py [-h] [--no_select]
[--radius-inc-step RADIUS_INC_STEP]
[--limit-clusters LIMIT_CLUSTERS]
file n
- file¶
ade.out
- n¶
# of total structures
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- --no_select¶
Don’t run selection once again. Use selected.out in the current folder
- --radius-inc-step <radius_inc_step>¶
radius incremental step, default 0.5
- --limit-clusters <limit_clusters>¶
# of clusters
rna_rosetta_cluster.py - cluster silent Rosetta files
A wrapper to ROSETTA tools for RNA modeling
Based on C. Y. Cheng, F. C. Chou, and R. Das, Modeling complex RNA tertiary folds with Rosetta, 1st ed., vol. 553. Elsevier Inc., 2015. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0076687914000524
rna_rosetta_cluster.py ade_min.out 20000
Take n * 0.005 (.5%) of all frames and put them into selected.out. Then the tool clusters this selected.out.
- rna_tools.tools.rna_rosetta.rna_rosetta_cluster.cluster(radius, limit_clusters)[source]¶
Internal function of cluster_loop: It removes cluster.out first.
- rna_tools.tools.rna_rosetta.rna_rosetta_cluster.cluster_loop(ns, radius_inc_step, limit_clusters)[source]¶
Go from radius 1 to get 1/6 of structures of ns (# of selected structures) in the first cluster, then it stops.
- rna_tools.tools.rna_rosetta.rna_rosetta_cluster.get_no_structures_in_first_cluster(fn)[source]¶
Get # of structures in a silent file.
- Parameters:
fn (string) – a filename to a silent file
- Returns
int: # of structures in a silent file
Minimize¶
rna_rosetta_min.py¶
rna_rosetta_min.py - a script to do minimization
The script takes the number of structures and the analyzed silence file and does the maths.
Job names will be as your silent file preceding with ~, .e.g ~tha.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0076687914000524
ade$ rna_rosetta_cluster.py ade.out
The first number states how many processors to use for the run, while the second number is 1/6 the total number of previously generated FARNA models. If you are running on a supercomputer that only allows specific multiples of processors, use an appropriate number for the first input.:
rosetta_submit.py min_cmdline min_out 1 24
rosetta_submit.py min_cmdline min_out [1] [16] The first number states how many processors to use for each line in min_cmdline. Here, enter 1 for the first input so that the total number of processors used will be equal to the number of processors entered with the “-proc” flag in command line [12], above. The second number states the maximum time each job will be allowed to run (walltime). Start the run with the appropriate command listed by the out- put above (e.g., source qsubMPI for the Stampede cluster).
E.g. for 20k silet file, 1/6 will be minimized = 3.3k:
parallel_min_setup.py -silent rp21cr62.out -tag rp21cr62_min -proc 200 -nstruct 3200 -out_folder mo -out_script MINIMIZE " -ignore_zero_occupancy false "
rosetta_submit.py MINIMIZE mo 1 100 m
[peyote2] rp21 easy_cat.py mo
Catting into: rp21_min.out ... from 200 primary files. Found 3200 decoys.
# on 200 cpus it took around ~30min
usage: rna_rosetta_min.py [-h] [-g] [-c CPUS] file
- file¶
ade.out
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- -g, --go¶
- -c <cpus>, --cpus <cpus>¶
default: 200
rna_rosetta_min.py - a script to do minimization
The script takes the number of structures and the analyzed silence file and does the maths.
Job names will be as your silent file preceding with ~, .e.g ~tha.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0076687914000524
ade$ rna_rosetta_cluster.py ade.out
The first number states how many processors to use for the run, while the second number is 1/6 the total number of previously generated FARNA models. If you are running on a supercomputer that only allows specific multiples of processors, use an appropriate number for the first input.:
rosetta_submit.py min_cmdline min_out 1 24
rosetta_submit.py min_cmdline min_out [1] [16] The first number states how many processors to use for each line in min_cmdline. Here, enter 1 for the first input so that the total number of processors used will be equal to the number of processors entered with the “-proc” flag in command line [12], above. The second number states the maximum time each job will be allowed to run (walltime). Start the run with the appropriate command listed by the out- put above (e.g., source qsubMPI for the Stampede cluster).
E.g. for 20k silet file, 1/6 will be minimized = 3.3k:
parallel_min_setup.py -silent rp21cr62.out -tag rp21cr62_min -proc 200 -nstruct 3200 -out_folder mo -out_script MINIMIZE " -ignore_zero_occupancy false "
rosetta_submit.py MINIMIZE mo 1 100 m
[peyote2] rp21 easy_cat.py mo
Catting into: rp21_min.out ... from 200 primary files. Found 3200 decoys.
# on 200 cpus it took around ~30min
- rna_tools.tools.rna_rosetta.rna_rosetta_min.get_no_structures(file)[source]¶
Get a number of structures in a silent file
- rna_tools.tools.rna_rosetta.rna_rosetta_min.min(silent_file, take_n, cpus, go)[source]¶
Run parallel_min_setup (to MINIMIZE file), rosetta_submit.py, and qsubMINI.
Fix on the way, qsub files:
-out:file:silent mo/0/mo/123/tha_min.out -> -out:file:silent mo/123/tha_min.out
I don’t know why mo/0/ is there. I might be because of my changes in rosetta_submit.py (?).
Extract lowscore decoy¶
rna_rosetta_extract_lowscore_decoys.py¶
rna_rosetta_extract_lowscore_decoys.py - a simple wrapper to extract_lowscore_decoys.py
To be used in Jupter notebooks and other scripts.
usage: rna_rosetta_extract_lowscore_decoys.py [-h] [-v] nstruc file
- nstruc¶
# of low score structures to obtained
- file¶
silent file
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- -v, --verbose¶
be verbose
rna_rosetta_extract_lowscore_decoys.py - a simple wrapper to extract_lowscore_decoys.py
To be used in Jupter notebooks and other scripts.
Check progress¶
rna_rosetta_cluster.py¶
rna_rosetta_check_progress.py - check progress for many simulations of Rosetta
Example:
[peyote2] rosetta_jobs rna_rosetta_check_progress.py .
jobs #curr #todo #decoys done
0 ./rp17s223 200 0 407 [ ]
1 ./rp17hcf 0 0 0 [ ]
# curr 232 #todo 0
usage: rna_rosetta_cluster.py [-h] [-v] [-m] [-s SELECT] [-k] dir
- dir¶
directory with rosetta runs, define by RNA_ROSETTA_RUN_ROOT_DIR_MODELING right now:
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- -v, --verbose¶
be verbose
- -m, --min-only¶
check only for mo folder
- -k, --kill¶
kill (qdel) jobs if your reach limit (nstruc) of structure that you want, right now is 10000 structures
rna_rosetta_check_progress.py - check progress for many simulations of Rosetta
Example:
[peyote2] rosetta_jobs rna_rosetta_check_progress.py .
jobs #curr #todo #decoys done
0 ./rp17s223 200 0 407 [ ]
1 ./rp17hcf 0 0 0 [ ]
# curr 232 #todo 0
SimRNA¶
Select low energy frames¶
rna_simrna_lowest.py¶
rna_simrna_lowest.py - get lowest energy frames out of a SimRNA trajectory file
This code uses heavily the SimRNATrajectory class. Be default 100 lowest energy frames is exported.
usage: rna_simrna_lowest.py [-h] [-n NSTRUC] trafl
- trafl¶
SimRNA trafl file
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- -n <nstruc>, --nstruc <nstruc>¶
SimRNA trafl file
Extract¶
rna_simrna_extract.py¶
rna_simrna_extra.py - extract full atom structures from a SimRNA trajectory file
Options:
SIMRNA_DATA_PATH has to be properly defined in
rpt_config_local.
usage: rna_simrna_extract.py [-h] -t TEMPLATE -f TRAFL [-c]
[-n NUMBER_OF_STRUCTURES]
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- -t <template>, --template <template>¶
template PDB file used for reconstruction to full atom models
- -f <trafl>, --trafl <trafl>¶
SimRNA trafl file
- -n <number_of_structures>, --number_of_structures <number_of_structures>¶
SimRNAweb¶
Download files of a SimRNAweb run¶
rna_simrnaweb_download_job.py¶
rna_simrnaweb_download_job.py - download model files, trajectory for a given SimRNAweb job.
Usage:
rp17pk$ rna_pdb_download_simrna_job.py 27b5093d -m -t -x
# download more clusters, trajectory, extract100
cp771_pk$ rna_pdb_download_simrna_job.py -t -x -m cf8f8bb2 -p cp771_pk
# download with a trajectory, and cluster #4 and #5, add to all pdb files
# prefix: cp771_pk
$ rna_simrnaweb_download_job.py --web-models rp17_well_d10_e1-a43d3ab5 --prefix tar
# prefix added will be tar_XXXX
Example:
rna_pdb_download_simrna_job.py -t -x -m 20569fa1 -p zmp_pk
[mm] zmp_pk ls
20569fa1_ALL_100low.trafl
_20569fa1-thrs7.10A_clust04
_20569fa1-thrs7.10A_clust05
_20569fa1_ALL_100low
data
rna_simrna_extract.log
subset.png
zmp_pk_20569fa1-thrs7.10A_clust01X.pdb
zmp_pk_20569fa1-thrs7.10A_clust02X.pdb
zmp_pk_20569fa1-thrs7.10A_clust03X.pdb
zmp_pk_20569fa1-thrs7.10A_clust04X.pdb
zmp_pk_20569fa1-thrs7.10A_clust05X.pdb
usage: rna_simrnaweb_download_job.py [-h] [-p PREFIX] [-n NSTRUC] [-e] [-m]
[-r] [-c] [-d] [--top100] [--top200]
[--web-models]
job_id
- job_id¶
job_id
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- -p <prefix>, --prefix <prefix>¶
prefix to the name, withouth _, be careful with this.If you have already some files with the given folder, their names mightbe changed.
- -n <nstruc>, --nstruc <nstruc>¶
extract nstruc the lowest energy, this option must go with –web
- -e, --extract¶
extract nstruc the lowest energy, this option must go with –web
- -m, --more_clusters¶
download also cluster 4 and 5
- -r, --remove-trajectory¶
remove trajectory after analysis
- -c, --cluster¶
get trajectory from cluster OR local on your computer (mdfind for macOS)
- -d, --download-trajectory¶
web
- --top100¶
download top100 trajectory
- --top200¶
download top200 trajectory
- --web-models¶
web models download
SimRNATrajectory¶
SimRNATrajectory module.
SimRNATrajectory / Frame / Residue / Atom
- class rna_tools.tools.simrna_trajectory.simrna_trajectory.Frame(id, header, coords, top_level=False)[source]¶
- Syntax of header:
write_number
replica_id
total_energy
energy_without_restraints
temperature
Warning
If there is an invalid frame, please use repair_trafl.py to fix the trajectory first.
- class rna_tools.tools.simrna_trajectory.simrna_trajectory.Residue(id, p, c4p, n1n9, b1, b2)[source]¶
Create Residue object.
Each residue in SimRNA coarse-grained represantation consists only 5 coarse-grained atoms:
backbone: p = phospate group, c4p = sugar moiety
nucleotide: n1n9 = N1 for pyrimidines, N9 for purines, b1 = C2 for purines and pyrimidines, b2 = C4 for pyrimidines, C6 for purines
- class rna_tools.tools.simrna_trajectory.simrna_trajectory.SimRNATrajectory[source]¶
- load_from_file(fn, debug_break=False, top_level=False, only_first_frame=False)[source]¶
Create a trajectory based on give filename.
- Parameters:
top_level –
top_level = True, don’t make a huge tree of objects (Residues/Atoms) == amazing speed up! Useful if you need only frames, energies and coords as text. You only get the info that is in header of each frame.
top_level = False, makes huge tree of objects (Residues/Atoms) == very slow for a huge trajectories
Warning
Loads up whole trafl file into memory, and get stuck. Use this if you want to compute e.g. distances between atoms, get the positions of specified atoms etc. If you can not process your trajectory
use top_level=True or look at load_from_string() to load a frame by frame from a file.
h(eader), l(line), f(ile)
RNA Refinement (QRNAS)¶
rna_refinement.py¶
rna_refinement - RNA refinement with QRNAS.
Models of RNA 3D structures obtained by modeling methods often suffer from local inaccuracies such as clashes or physically improbable bond lengths, backbone conformations, or sugar puckers. To ensure high quality of models, a procedure of re nement should be applied as a nal step in the modeling pipeline. The software tool QRNAS was developed in our laboratory to perform local re nement of nucleic acid structures based on an extended version of the AMBER force field. The extensions consist of energy terms associated with introduction of explicit hydrogen bonds, idealization of base pair planarity and regularization of backbone conformation.
Read more: Piatkowski, P., Kasprzak, J. M., Kumar, D., Magnus, M., Chojnowski, G., & Bujnicki, J. M. (2016). RNA 3D Structure Modeling by Combination of Template-Based Method ModeRNA, Template-Free Folding with SimRNA, and Refinement with QRNAS. Methods in Molecular Biology (Clifton, N.J.), 1490(Suppl), 217-235. http://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6433-8_14
Right now, there is 20k steps of refinement.
The initial structure, 179c48aa-c0d3-4bd6-8e06-12081da22998_ALL_thrs6.20A_clust01-000001_AA.pdb.
after 3k, ~10min
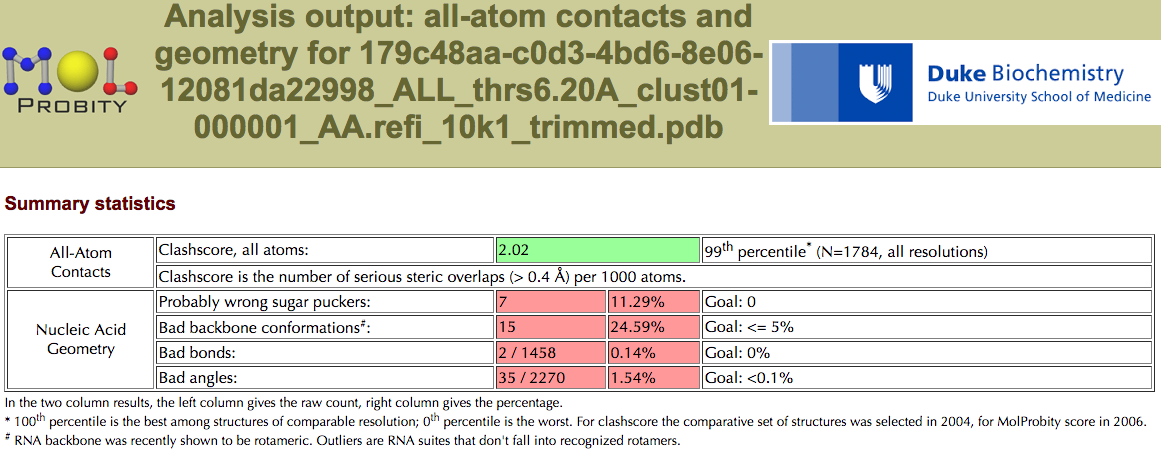
after 10k steps, around 30min
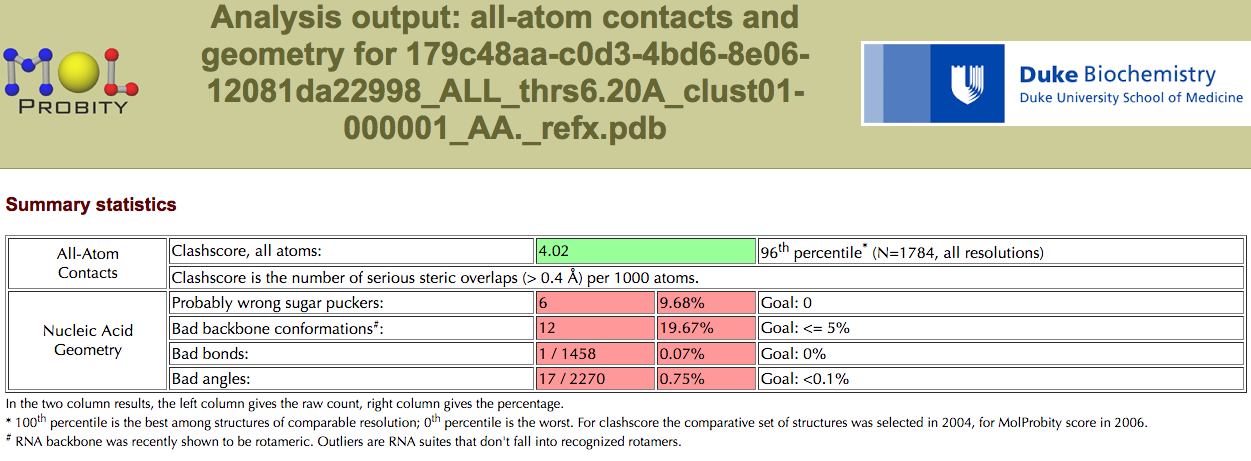
after 20k steps, around 1h.
Installation of QRNAS
Download the QRNAS package from http://genesilico.pl/qrnas/, unzip the archive, and compile it with the following command:
./qrnamake sequential
This should create an executable version of QRNAS.
Warning
Please, change the name of the binary file from QRNA to QRNAS!
Be default the script searches QRNAS in <rna-tools>/opt/qrnas/ .
Usage of QRNA:
QRNA - Quick Refinement of Nucleic Acids (0.2 alpha)
by Juliusz Stasiewicz (jstasiewicz@genesilico.pl)
To use type:
QRNA -i <input PDBfile> [-o <output PDBfile>] [-c <configfile>] [-p] [-m <restraintsfile>]
OR specify <input PDBfile>, <output PDBfile> and <restraintsfile> in <configfile> and type just:
QRNA -c <configfile>
Installation of this util
Set up in your bashrc:
export QRNAS_PATH=<your path to qrnas> # e.g. /home/magnus/src/rna-tools/opt/qrnas
but default rna-tools searches for qrnas in <rna-tools>/opt/qrnas.
QRNAS at Peyote2
There is no problem to run QRNAS at our Genesilico cluster, peyote2. Tested by mmagnus –170822. Copy files of QRNAS to peyote and run ./qrnamake sequential.
To run it at a cluster with the Sun Grid Engine queuing system (this one with qusb ;-)):
for p in *.pdb; do echo "rna_refinement.py $p >& ${p}.log" | qsub -cwd -V -pe mpi 1 -N "r_$p" ; done
DONE:
[x] clean up the output structure
[x] configuration should not be hardcoded
usage: rna_refinement.py [-h] [-s STEPS] [-o OUTPUT_FILE] [-i] [-v] fn
- fn¶
input pdb file
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- -s <steps>, --steps <steps>¶
# of steps, default: 20k
- -o <output_file>, --output_file <output_file>¶
output pdb file
- -i, --interactive¶
- -v, --verbose¶
RNA Molecular Dynammics (MD)¶
diffpdb¶
diffpdb - a simple tool to compare text-content of PDB files
The method is quick-and-dirty, but works!
The script takes first 31 characters of lines (or only atom names and residue names)
starting with HETATM or ATOM and save these lines to a <filename>.out file.
One file is created per pdb. In the final step DIFF_TOOL is executed on these two output files. You get a diff output. That’s it! Enjoy!
Configuration:
DIFF_TOOL="open -a diffmerge"orDIFF_TOOL="kompare"to set up what tool would you like to use to diff files in the filerna-pdb-tools/tools/diffpdb/diffpdb_conf.py(create it if needed)
./diffpdb.py --names test_data/4/1duq.pdb test_data/4/1duq_decoy0171_amb_clx.pdb
and on the Mac (using diffmerge):
One of the difference that can be detected with the script is variants of atoms.
or a detection of missing atom.
or a detection of missing OP3 at the beginning.
RNA clustering with CLANS (clanstix)¶
rna_clanstix - a tool for visualizing RNA 3D structures based on pairwise structural similarity with Clans.
We hacked Clans thus instead of BLAST-based distances between sequences, you can analyze distances between structures described as p-values of rmsd (based on the method from the Dokholyan lab.)
Quickref:
rna_clanstix.py --groups-auto 10 --color-by-homolog --shape-by-source thf_ref_mapping_pk_refX.txt input2.clans
Running Clans: To run CLANS you need to have Java 1.4 or better installed (java can be downloaded HERE). For full functionality you will also need the NCBI BLAST,PSI-BLAST and formatdb executables (NCBI). For command line parameters and basic help please refer to the README file. (source: http://www.eb.tuebingen.mpg.de/research/departments/protein-evolution/software/clans.html)
The RMSDs between structures are converted into p-values based on the method from the Dokholyan lab or some hacky way developed by mmagnus .
Color groups¶
You can color your groups:
To get colors, run a cmd like this:
rna_clastix.py rnapz17_matrix_farfar_HelSeedCst.txt --groups 20:seq1+20+20+20+20+20+20:seq10
where with the + sign you separate groups. Each group has to have a number of structures. Optionally it can have a name, e.g., 20:seq1, use : as a separator. If a provided name is native then this group will be shown as starts.
Get inspiration for more colors (http://www.rapidtables.com/web/color/RGB_Color.htm)
How to use ClanstixRNA?¶
Get a matrix of distances, save it as e.g. matrix.txt (see Comment below)
run ClanstixRNA on this matrix to get an input file to Clans (e.g. clans_rna.txt):
rna_clanstix.py test_data/matrix.txt # clans.input will be created by default
open CLANS and click File -> Load run and load clans_run.txt
You’re done! :-)
Comment: To get this matrix you can use for example another tool from the rna-pdb-tools packages:
rna_calc_rmsd_all_vs_all.py -i rp18 -o rp18_rmsd.csv
rna_clastix.py --groups 1:native+5:3dRNA+
5:Chen+3:Dokh+5:Feng+5:LeeASModel+
5:Lee+5:RNAComposer+10:RW3D+5:Rhiju+
1:YagoubAli+3:SimRNA rp18_rmsd.csv clans.in
rna_clastix.py --groups 100+100+100+100+100+100+100+100+100+100+1:native rp18_rmsd.csv
where rp18 is a folder with structure and rp18_rmsd.csv is a matrix of all-vs-all rmsds.

Hajdin, C. E., Ding, F., Dokholyan, N. V, & Weeks, K. M. (2010). On the significance of an RNA tertiary structure prediction. RNA (New York, N.Y.), 16(7), 1340–9. doi:10.1261/rna.1837410
An output of this tool can be viewed using CLANS.
Frickey, T., & Lupas, A. (2004). CLANS: a Java application for visualizing protein families based on pairwise similarity. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England), 20(18), 3702–4. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bth444
- class rna_tools.tools.clanstix.rna_clanstix.RNAStructClans(n=10, dotsize=10)[source]¶
Clans run.
Usage:
>>> f = open('matrix.txt') >>> ids = f.readline().replace('#','').split() >>> c = RNAStructClans(n=len(ids)) # 200? >>> c.add_ids(ids) >>> c.dist_from_matrix(f) >>> print(c.txt)
- rna_tools.tools.clanstix.rna_clanstix.check_symmetric(a, rtol=1e-05, atol=1e-08)[source]¶
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/42908334/checking-if-a-matrix-is-symmetric-in-numpy
Misc¶
Plotting¶
rna_plot_hist.py¶
rna_plot_hist.py - generate a histogram
Don’t open Excel, Jupyter. Simple plot a histogram of one column and save it to a file.
Example:
# file
fn rmsd_all
0 19_Bujnicki_Human_4_rpr_n0-000001.pdb-000001_A... 14.73
1 19_Bujnicki_Human_4_rpr_n0-000001.pdb.trafl_19... 0.46
2 19_Bujnicki_Human_4_rpr_n0-000001.pdb.trafl_19... 14.73
3 19_Bujnicki_Human_4_rpr_n0-000001.pdb_thrs0.50... 0.73
4 19_Bujnicki_Human_4_rpr_n0-000001.pdb_thrs0.50... 0.83
$ rna_plot_hist.py rmsds.csv --column rmsd_all
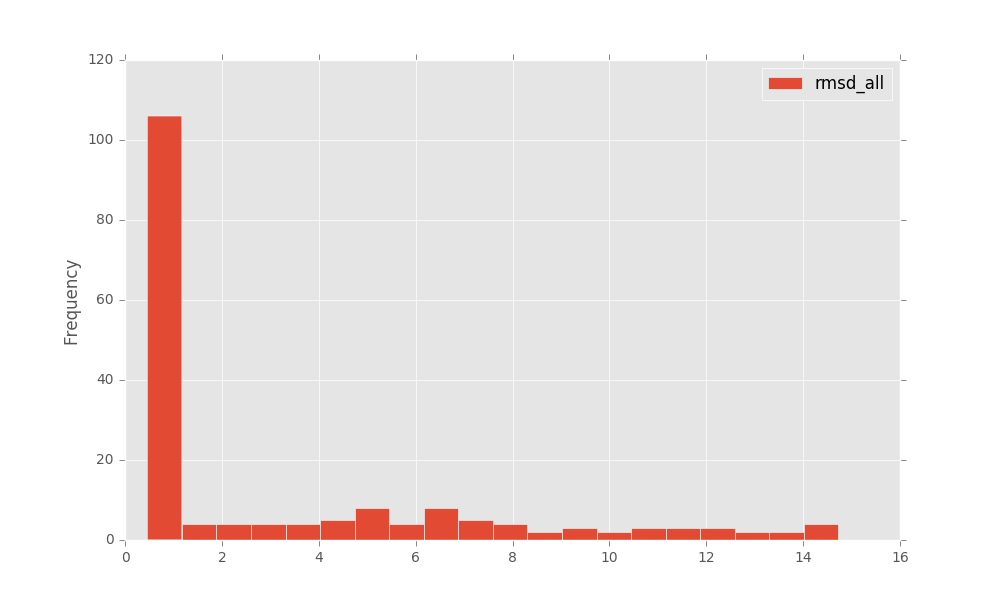
usage: rna_plot_hist.py [-h] [--column COLUMN] [--sep SEP] [-o OUTPUT]
[--bins BINS]
file
- file¶
rmsd.txt
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- --column <column>¶
column of file to plot
- --sep <sep>¶
separator, be default
- -o <output>, --output <output>¶
- --bins <bins>¶
rna_plot_density.py¶
rna_plot_density.py - generate a density plot
Don’t open Excel, Jupyter. Simple plot a density of one column and save it to a file.
Example:
# file
fn rmsd_all
0 19_Bujnicki_Human_4_rpr_n0-000001.pdb-000001_A... 14.73
1 19_Bujnicki_Human_4_rpr_n0-000001.pdb.trafl_19... 0.46
2 19_Bujnicki_Human_4_rpr_n0-000001.pdb.trafl_19... 14.73
3 19_Bujnicki_Human_4_rpr_n0-000001.pdb_thrs0.50... 0.73
4 19_Bujnicki_Human_4_rpr_n0-000001.pdb_thrs0.50... 0.83
$ rna_plot_hist.py rmsds.csv --column rmsd_all
usage: rna_plot_density.py [-h] [--column COLUMN] [--sep SEP] [-o OUTPUT] file
- file¶
rmsd.txt
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
- --column <column>¶
column of file to plot
- --sep <sep>¶
separator, be default
- -o <output>, --output <output>¶
rna_sali2dotbracket¶
rna_sali2dotbracket¶
usage: rna_sali2dotbracket [-h] filename
- filename¶
file in the Sali format
- -h, --help¶
show this help message and exit
This beauty here will go to sali notation and convert it to dotbracket notation. The file name should be xxxx.sali
Author: Catarina Almeida
- rna_tools.tools.rna_sali2dotbracket.rna_sali2dotbracket.convert_sali2dotbracket(fn)[source]¶
The function needs a filename in the Sali format. This function will get the secondary structure of the sequence, then get its identifier and then the sequence itself.
To get the ss
The line with the secondary structure is a list and will look like this:
['', '', '', '', '', '', '', '', '', '', '--...<<<[[...]]..>>>>', '', '', '\n']
In this case, the ss is in the 11th position. But in some files it may be in the 12th, 13th, 10th, etc..
If the longest element from the list is extracted, then this problem is overcomed.
The ss will some times have patterns of repeated gaps, which will come in the form of:
x
xnt
( x )
With x being any number, from 1 to 1000. These must be converted to the correspondent number of gaps (-) in the converted ss. This conversion is done by:
1 - Identifying the pattern with regex
2 - Replacing it with repl function.
As such, the following expressions will replace the previously mentioned patterns:
re.sub(r'\d*\d', repl, temp)re.sub(r'\d*\dnt', repl, temp)re.sub(r'(?P<smthBeautiful>\(\d+\))', repl, temp)
To get the sequence
The sequence, much like the ss, can sometimes be in a different position in the list. Like in the ss, the longest element will be selected. Also, like in the ss, patterns for repeated gaps appear. So these must also be removed.
Cluster load¶
A very simple tool to see your cluster load per user:
MAX_JOBS: 1000
#jobs cluster 917 load: 0.917 to use: 83
#jobs you 749 load: 0.749 to use: 251
{'deepak': 160, 'azyla': 8, 'magnus': 749}
1 azyla r 8
20 magnus r 10
16 deepak r 10
329 magnus r 1
22 magnus qw 10
A super simple script to get some statistics of who is running at a cluster
Set MAX_JOBS to calc % of usage, it’s an approximation of max number of jobs, e.g. peyote ~1k (rather 700, e.g. FARNA runs.).